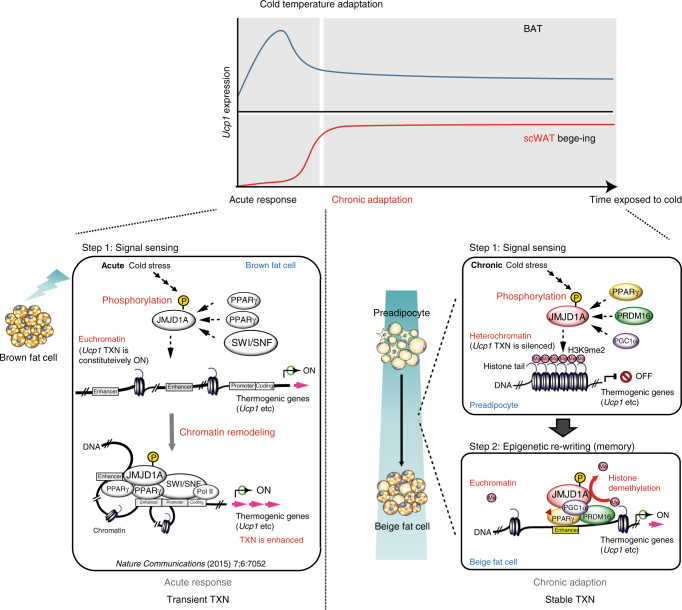
Fig. 8.
Complementary mechanisms for thermogenic gene induction in acute and chronic cold stress via overlapping, but distinct mechanisms of JMJD1A. Brown fat cells mediate acute and robust thermogenic activation of Ucp1, while scWAT-derived beige fat cells contribute to an adaptive response against chronic cold exposure (top). The acute response in BAT requires a BAR-dependent phosphorylation of JMJD1A that facilitates long-range enhancer-promoter interactions and stimulate thermogenic gene expressions, but this does not require the intrinsic H3K9me2 demethylation activity of JMJD1A (left bottom). The chronic adaptation in beigeing requires both phosphorylation-dependent chromatin recruitment and H3K9me2 demethylation activity of JMJD1A (right bottom). These histone demethylation-independent acute Ucp1 induction in BAT and demethylation-dependent chronic Ucp1 expression in beige scWAT ensure an ordered transition between acute and chronic adaptation to cold stress. TXN transcription