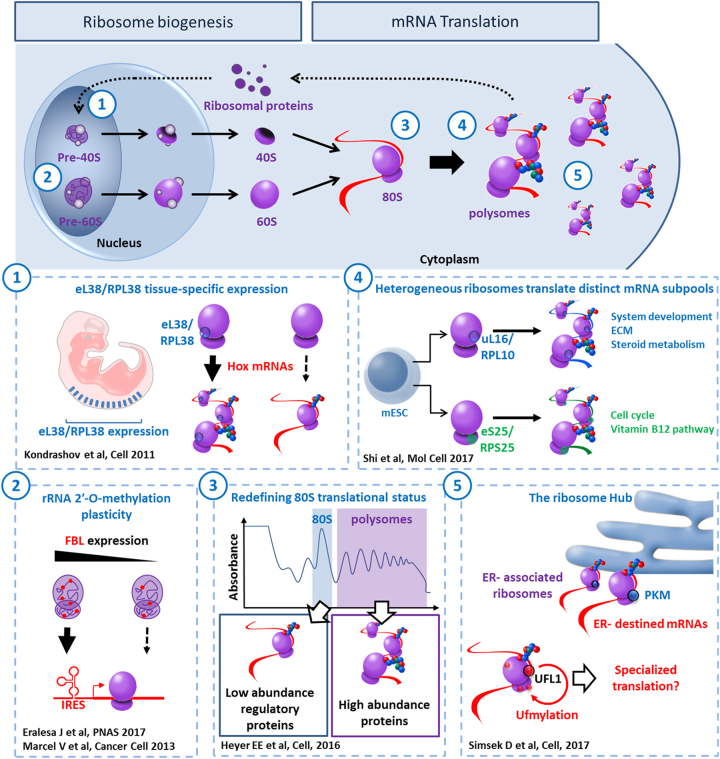
Fig. 1. The multifaceted ribosome.
The top banner gives an overview of ribosome biogenesis and mRNA translation. Along this process, each number refers to an illustration of ribosome heterogeneity and its corresponding impact on ribosome function. (1) In mouse, distribution pattern of mRNA encoding RPs varies significantly from one tissue to another. In particular, eL38/RPL38 expression is enriched in developing somites and neural tube. eL38/RPL38 is essential for translating specific Hox mRNAs that are involved in axial skeletal patterning. (2) During ribosome biogenesis, 2-O-methylation of the ribose is performed by the methyltransferase Fibrillarin (FBL). In human cells, any change in FBL expression may affect a repertoire of 2′-O-methylation sites showing plasticity. This translates into modulation of the intrinsic capabilities of ribosomes to engage IRES-containing mRNAs. (3) A recent ribosome profiling analysis preformed in S. cerevisiae revealed that, contrary to common belief, the vast majority of 80S monosomes were actively translating. Furthermore, besides translating short ORFs, uORFs, and Nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) targets, this ribosome population is specialized in synthesizing key regulatory proteins, such as transcription factors, kinases, and phosphatases. (4) Ribosome heterogeneity is observable at the sub-cellular level in murine embryonic stem cells. Differences in RPs composition bestow differential selectivity to translate mRNAs subpools. For instance, controlling the amount of uL16/RPL10A containing ribosomes participates in regulating expression of specific genes involved in metabolism, extra-cellular matrix (ECM) organization, cell cycling and development. (5) The surface exposed rRNA shell of eukaryotic ribosome provides an ideal interface for interacting proteins. Pyruvate kinase muscle (PKM) interacts with a sub-pool of endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-associated ribosomes and promotes translation of targeted mRNAs. UFL1 association with ribosome results in ufmylation of several RPs (uL16/RPL10, uS10/RPS20, and uS3/RPS3) and may be involved in subunit joining and contribute to transcript-specific translation