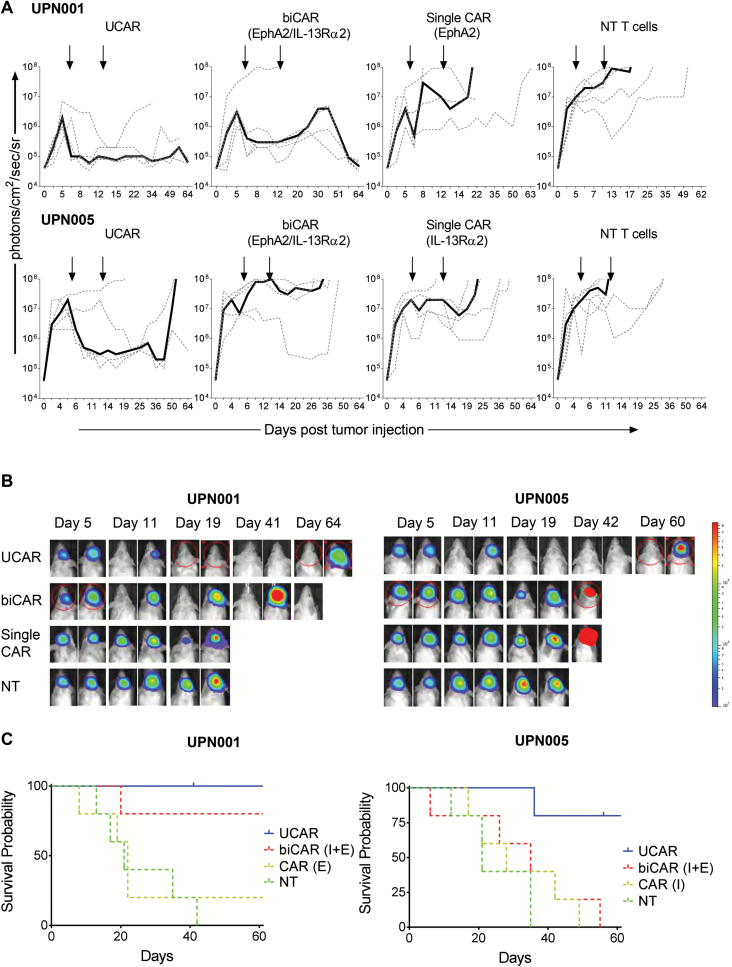
Fig. 5.
In vivo experiments demonstrate superior antitumor activity and survival in UCAR-treated mice in an autologous tumor model; 2.5 × 105 patient GBM cells were stereotactically injected into the right caudate nucleus of SCID mice. On days 5 and 12 after tumor cell injection (indicated by arrows), mice received an intratumoral injection of 3 × 106 autologous best single CAR (IL13Rα2), best biCAR (IL13Rα2 and EphA2), UCAR T cells, or NT T cells normalized for transduction efficiency. (A) Bioluminescence imaging to monitor tumor size for mice injected with 2 patient primary tumor samples and followed by treatment with UCAR, biCAR, single CAR, and NT T cells derived from the same patient’s peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Median bioluminescence (solid line) and individual mouse data (dashed lines) are shown for mice in each group (n = 5 for each group). (B) Representative images of the bioluminescence imaging to monitor tumor size. (C) Kaplan–Meier curves for the in vivo experiments followed to 60 days post tumor injection.