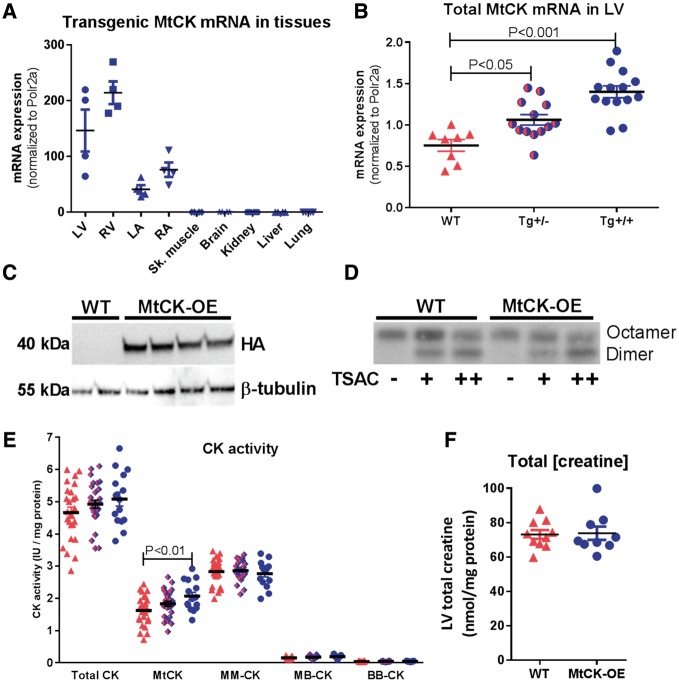
Figure 1.
Model validation at mRNA, protein, and enzymatic activity levels. (A) Transgenic MtCK mRNA expression in a panel of tissues from MtCK over-expressing mice indicating cardiac specificity for ventricles (LV, RV) and atria (LA, RA) (n = 2 M/2 F per tissue). (B) Quantitative RT-PCR for total MtCK transcript levels in LV illustrating gene dosing in wild-type (WT, n = 5 M/3 F), hemizygous (Tg+/-, n = 9 M/4 F), and homozygous mice (Tg+/+, n = 6 M/8 F). (C) Western blot showing detection of transgenic protein via haemagglutinin tag in LV tissue from Tg+/+ (n = 4 male), but not WT mice. (D) Incubation of mitochondrial fraction with transition site analogue complex (TSAC) to convert MtCK from octameric to dimeric form, suggesting that under normal conditions all detectable MtCK is in the octameric form in both WT and Tg mice (representative blot from n = 3 repeats). (E) Activity of the mitochondrial CK isoenzyme is significantly elevated in a gene dose-dependent fashion, with no change in other CK isoforms (shown in order WT n = 25; Tg+/-n = 28; Tg+/+n = 15). (F) LV total creatine levels are not significantly altered by over-expression of MtCK (WT n = 10; Tg+/+n = 9). Data are represented as mean ± SEM.