Figure 3. Improved de novo prediction of side-chain conformations with explicit solvent.
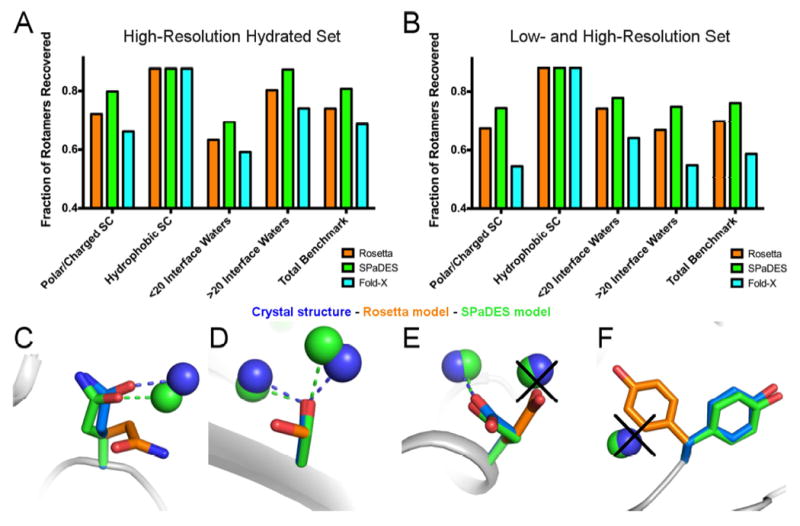
(A, B) Fraction of experimentally-observed side-chain conformations recovered using either Rosetta (orange), SPaDES (green), Fold-X with explicit water molecule modeling (cyan) for the high-resolution hydrated (A) and low- and high- resolution (B) set of protein-protein complex structures. Side-chain rotamer recovery is reported for specific classes of residues: polar and charged side-chains, hydrophobic side-chains, side-chains at protein-protein binding interfaces with less than 20 waters, and side-chains at protein-protein binding interfaces with more than 20 interface waters. (C-F) Improved side-chain conformation predictions using SPaDES are shown for (C) a glutamine in UCH-L3, (D) a serine in SHV-1 beta-lactamase, (E) a glutamic acid in TEM-1 beta-lactamase, and (F) a tyrosine in BLIP. Dotted lines indicate hydrogen bonds for the corresponding colored structures and black crosses indicate clashes between the Rosetta prediction and the experimentally-resolved waters. See also Table S2.
