Figure 4.
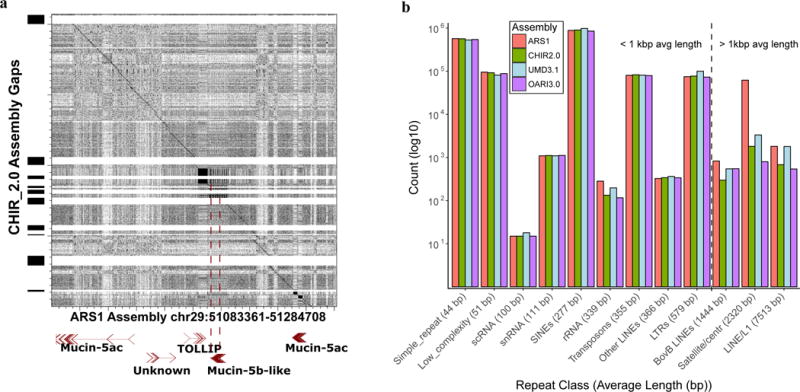
Long-read assembly with complementary scaffolding resolves gap regions (A) and long repeats (B) that cause problems for short-read reference annotation. (A) A region of the Mucin gene cluster was resolved by long-read assembly, resulting in a complete gene model for Mucin-5b-Like that was impossible due to two assembly gaps in the CHIR_2.0 assembly. (B) Counts of repetitive elements that had greater than 75% sequence length and greater than 60% identity with RepBase database entries for ruminant lineages. With the exception of the rRNA cluster (which is present in many repeated copies in the genome), the CHIR_2.0 reference contained a full complement of shorter repeat segments that were also present in our assembly. However, repeats that were larger than 1 kb were present in higher numbers in our assembly due to our ability to traverse the entire repetitive element’s length.
