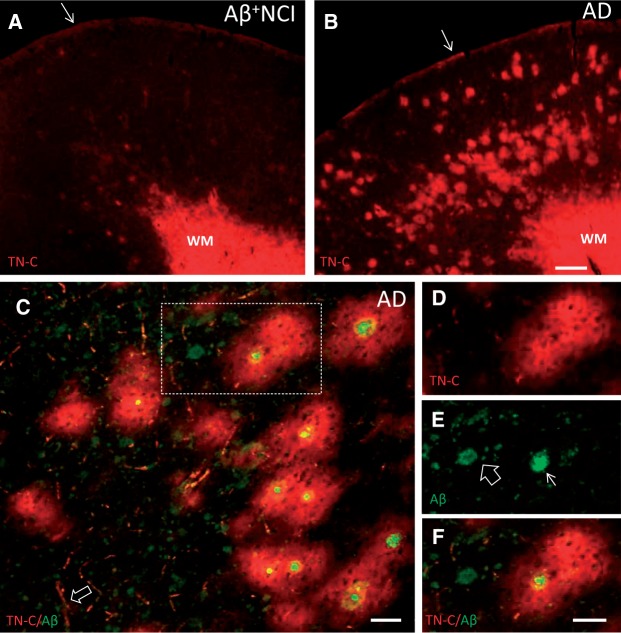
FIGURE 1.
TN-C immunofluorescence in the frontal cortex from representative Aβ plaque burdened NCI (A) and AD (B) cases. Dense TN-C ir is present in the WM and subpial layer (arrows) in both cases, whereas TN-C deposits in the gray matter are more abundant in AD. (C) Section of frontal cortex from an AD case processed for dual immunofluorescence with antibodies against TN-C (red) and Aβ (green) showing that the majority of large TN-C deposits completely surround cored Aβ plaques. TN-C-labeled blood vessels are also seen (arrow). (D-F) TN-C/Aβ dual-immunolabeling in the area boxed in C . TN-C ir (D, red) surrounds the cored Aβ plaque (arrow in E , green) while the diffuse Aβ plaque (open arrow in E , green) is not associated with TN-C ir. Merged image is shown in (F) . Scale bars: bar in A = 500 µm (for A and B ); bar in C =50 µm; bar in D = 50 µm (for D - F ).