Figure 3.
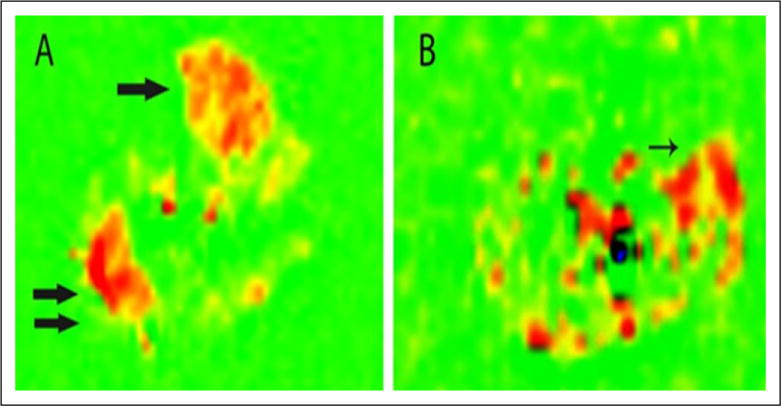
Pulsed arterial spin-labeling of a calf in a normal patient (A) and patient with peripheral artery disease (B) after peak exercise. Flow is increased in the anterior tibialis (single arrow) and lateral gastrocnemius (double arrow) muscles of the normal patient. The patient with peripheral artery disease has the highest flow signal in the peroneus longus muscle (arrow). Reprinted from [48] with permission from Elsevier.
