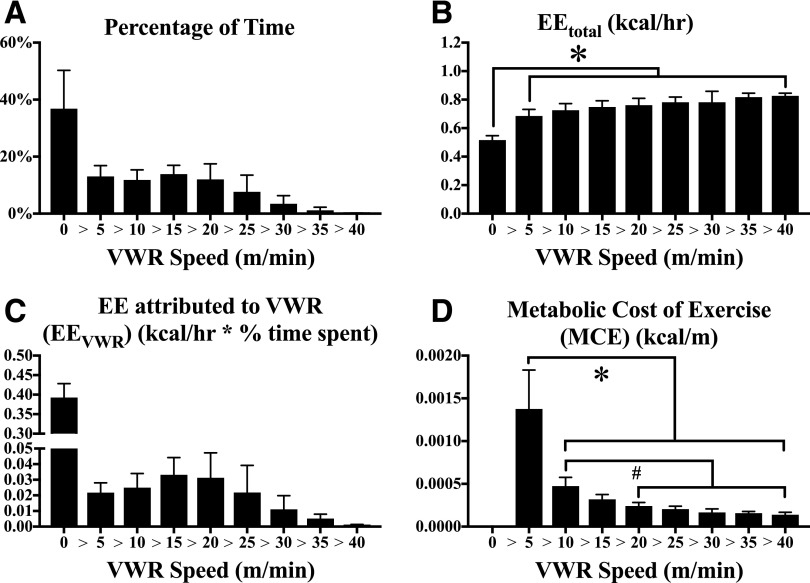
Figure 2.
Acute changes in EE and metabolic efficiency as a function of VWR speed. Real-time data from each mouse (435 data points/mouse) over the final three dark phases of the experimental period were separated based on running speed over each 5-min interval. The fraction of time mice spent inactive (VWR = 0) or running at different VWR speeds was measured (A). EEtotal of mice during inactivity or at various VWR speeds was determined (B). The fraction of EEtotal attributed to VWR at a given speed (active EE − inactive EE) was multiplied by the time spent at that speed to determine the contribution of VWR to EEtotal (EEVWR) (C). MCE (kcal/m traveled) was determined by dividing EEVWR by the distance traveled at each speed (D). N = 12 mice; * or #P < 0.05 between bracketed groups. hr, hour.