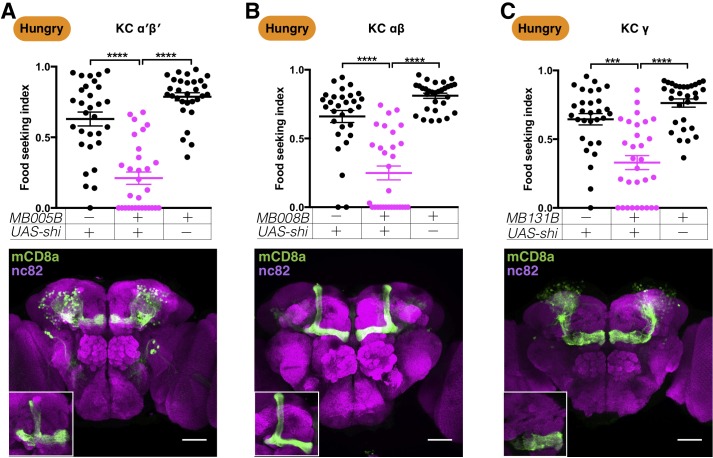
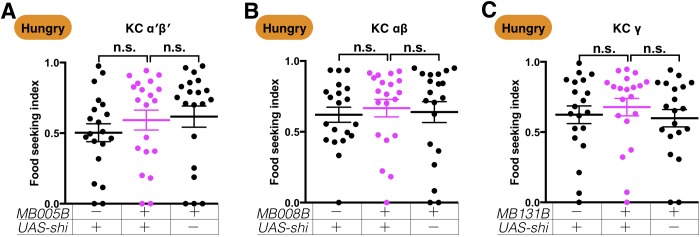
Figure 2. Kenyon cells are required for yeast food-seeking behavior in hungry flies.
(A–C) Male flies starved for 24 hr were assessed for their yeast food-seeking performance. The performance of GAL4;UAS-shits1 flies was statistically different from the controls for (A) MB005B split-GAL4 (α′β′ KCs; Kruskal-Wallis, n = 30, p<0.0001), (B) MB008B split-GAL4 (αβ KCs; Kruskal-Wallis, n = 30, p<0.0001), and (C) MB131B split-GAL4 (γ KCs; Kruskal-Wallis, n = 30, p=0.0003). Individual data points and mean ± SEM are shown. The brain images are full z-projections of confocal stacks showing the expression patterns of the GAL4 lines (green) counter-stained with nc82 antibody (magenta). Insets are z-projections of the MB lobes. Scale bars are 100 µm.