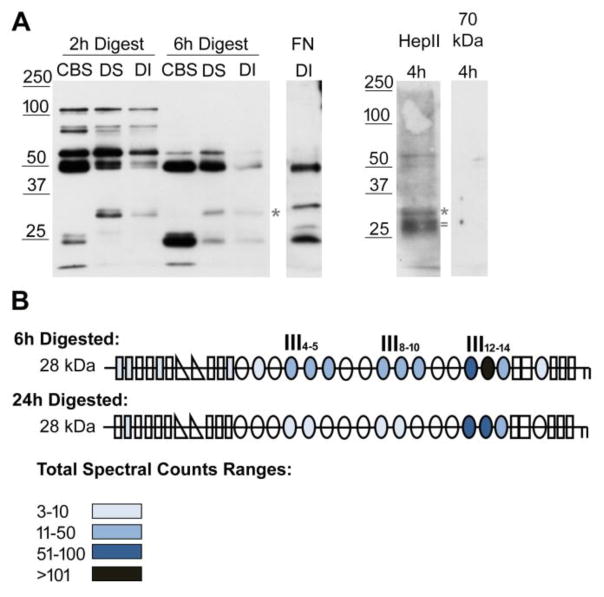
Figure 6. Identification of FN domains in DOC-insoluble matrix fibril fragments.
(A) Decellularized matrices from NIH3T3 fibroblasts were subjected to 2 h or 6 h proteolysis with chymotrypsin followed by detergent solubilization. Cleavage buffer soluble (CBS), DOC-soluble (DS), and DOC-insoluble (DI) matrix fractions were separated by SDS-PAGE on a 10 % polyacrylamide gel. FN fragments were detected by immunoblotting 2 h and 6 h digests with anti-III1–6 antiserum (R184). The sample in the FN DI lane was digested for 9 h and was immunoblotted with anti-full length rat FN antiserum (R39). DI samples after 4 h of digestion were immunoblotted with anti-(HepII) antiserum or anti-70 kDa antiserum (R457, 1:250 dilution) to visualize FN specific fragments. Anti-HepII antibodies detected band(s) between 25 and 32 kDa, which are not apparent in the anti-III1–6 blot. Asterisks denote the band at ~ 32 kDa and = marks the ~ 28 kDa band referred to in the text. (B) Fragments of about 28 kDa (between 25 and 32 kDa) from 6 h and 24 h digestions of decellularized matrix were submitted for mass spectrometry. Schematics of FN modules are colored-coded to indicate the total number of spectra from all the FN peptides identified in each of the modules. See color legend for ranges of total spectral counts. The majority of peptides were localized in the HepII domain (III12–14) but, at 6 h, fragments containing III4–5 and III8–10 were also detected.