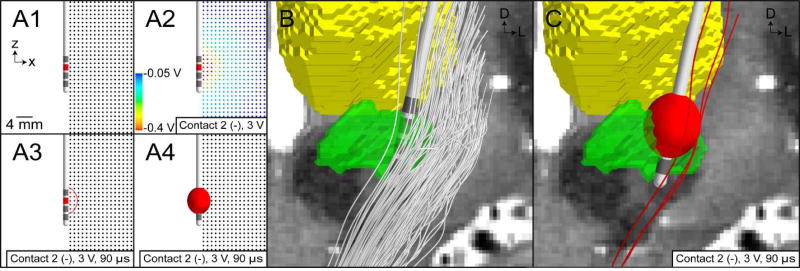
Figure 4.
VTA PAM for subthalamic DBS. (A) Illustrative example of training a VTA algorithm with an axisymmetric model of DBS. (A1) Multi-compartment cable models of straight axons perpendicular to the electrode are modeled. (A2) The potential distribution from a volume conductor model with isotropic and homogeneous conductivities is used to stimulate the model axons. (A3) Those axons that are activated by stimulation are shown as red. A circumscribing ellipse is then used to characterize the spatial extent of activation. (A4) The ellipse is then extruded about the electrode shaft to create an ellipsoid volume. (B) Trajectories of internal capsule fibers of passage are generated using probabilistic tractography. (C) VTA mapped to the patient-specific location of the DBS electrode, and the trajectories of axons that intersect the VTA are categorized as active (red streamlines).