Fig. 1.
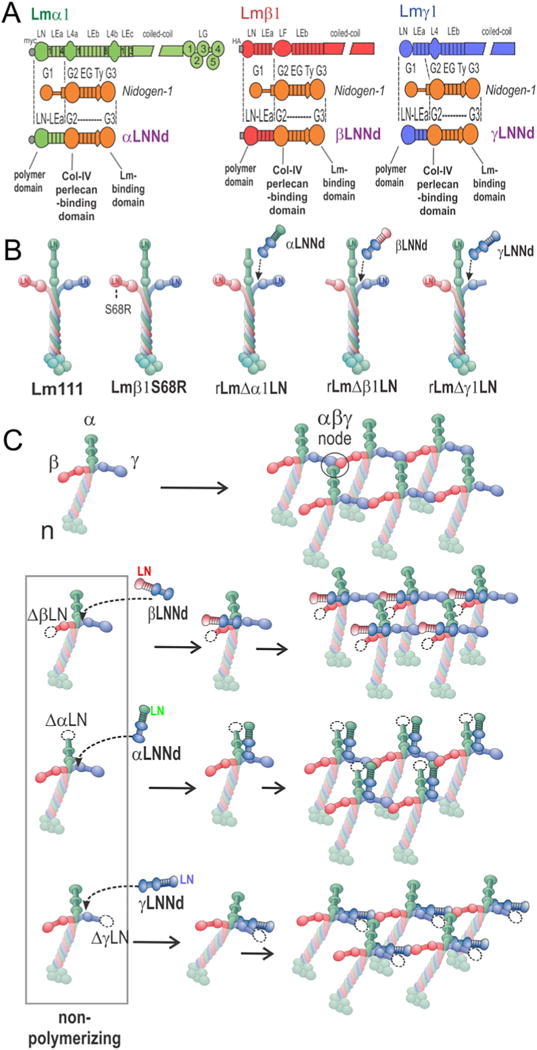
xLNNd and laminin proteins. A. Construct design for chimeric hybrids consisting of β1, α1 and γ1 laminin LN-LEa domains fused to the nidogen-1 G2 through G3 domains. B. Recombinant α1β1γ1 laminins, wild-type (WT) and bearing an S68R point mutation or with α, β or γ1 mutations used in the study. C. Laminin polymerizes through the binding of α, β and γ LN domains, forming a ternary node complex. Laminins lacking any of the three LN domains are unable to polymerize. Polymerization can be restored to these proteins by binding to corresponding α, β, and γLNNd proteins that provide the missing domain in an artificial short arm.
