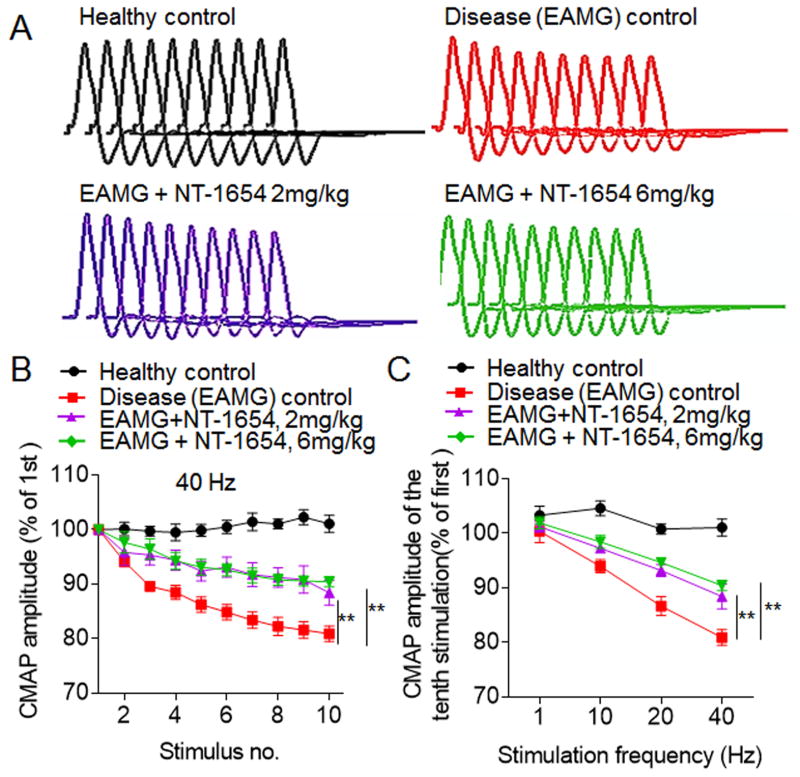
Figure 2. NT-1654 treatment attenuates CMAP decrement in EAMG rats.
CMAPs in the tibialis anterior were recorded in response to a train of 10 submaximal stimuli at different frequencies in control and EAMG rats at day 49 after immunization. The first stimulus response in control rats was designated as 100%. (A) Representative CMAP traces in response to 10 successive stimulations at 40 Hz for healthy control, EAMG + vehicle, EAMG + NT-1654 (2 mg/kg), and EAMG + NT-1654 (6 mg/kg) rats. (B) Effects of NT-1654 on CMAP decrement in EAMG rats. NT-1654 attenuated the decrement of CMAP amplitudes at 40 Hz in EAMG rats. (C) NT-1654 CMAP attenuated the decrement of CMAP amplitudes of the tenth stimulation at different stimulation frequencies. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m.; n = 12 rats per group; **p<0.01.