Fig. 3.
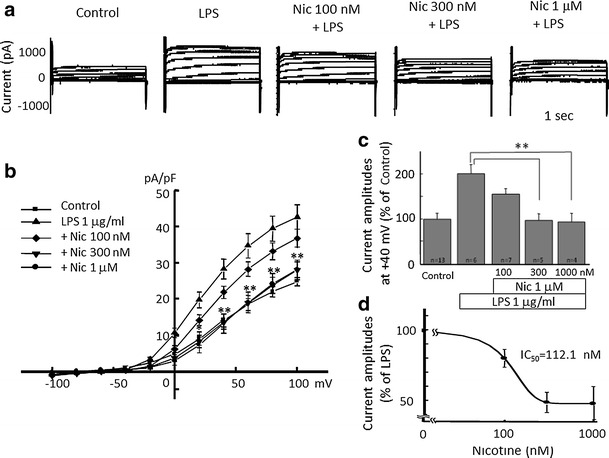
Nicotine dose-dependently attenuates LPS-induced microglial H+ currents. a Current traces from −100 to +100 mV from the holding potential of −60 mV for 1 s are shown. Application of LPS (1 μg/ml) was for 24 h and nicotine at concentration of 100 nM, 300 nM, and 1 μM were pre-treated for 1 h before application of LPS. b I–V relationships in the absence of LPS (control, filled square), with 1 μg/ml LPS (filled upright triangle), LPS with 100 nM (open diamond), 300 nM (filled downright triangle), and 1 μM Nic (filled circle) are shown. c The relative current amplitudes at +40 mV in b are shown. d Dose-dependent effect of Nic on LPS-induced microglial H+ currents is shown. The half inhibitory concentration (IC50) of Nic is 112.13 nM. **p < 0.01 compared to LPS (1 μg/ml)
