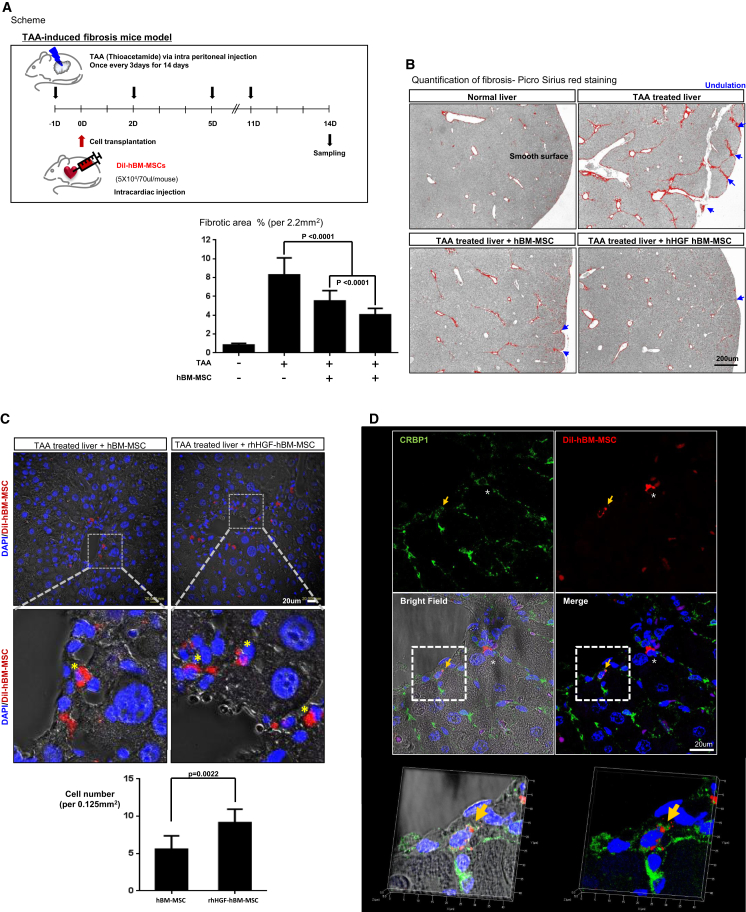
Figure 6.
rHGF Treatment Enhances the Therapeutic Efficacy of hBM-MSCs
(A) Experimental scheme of the systemic administration of rHGF-treated hBM-MSCs via intracardiac injection into the livers of TAA-treated mice. (B) Picrosirius red staining of fibrotic areas at 14 days after cell transplantation. TAA-induced liver fibrosis was significantly prevented by transplantation of hBM-MSCs and even more so by transplantation of rHGF-treated hBM-MSCs. Means with error bars for n = 5, measured fibrotic area in 3 pictures taken at random from each group. The bars show SD and present plus value only. (C) Confocal microscopy images of liver tissues after 14 days showed the persistence of systemically administered hBM-MSCs in the liver. DiI-labeled hBM-MSCs were counted in liver tissues at 14 days after systemic administration. rHGF treatment improved the homing, engraftment, and survival of hBM-MSCs (p = 0.0022). Means with error bars for n = 5, measured cells in 3 pictures taken at random from each group and calculated cell number per 0.125 mm2. The bars show SD, and present plus value only. (D) Immunostaining of transplanted hBM-MSCs to determine their fate. CRBP1 was used as a marker of quiescent HSCs.