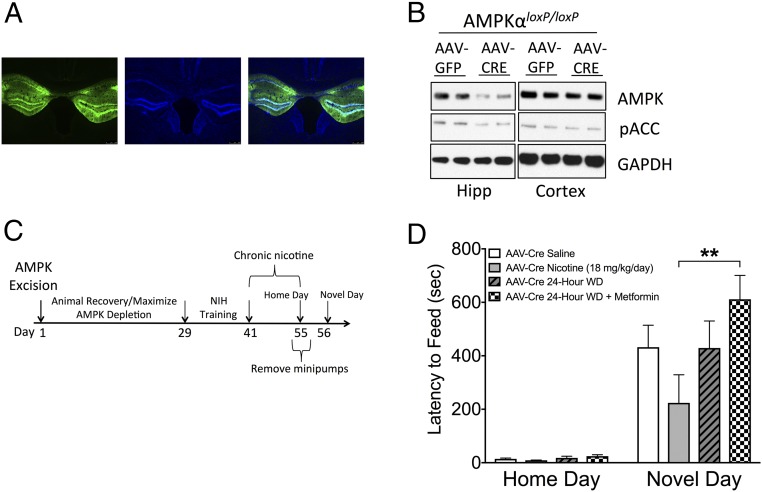
Fig. 4.
Anxiolytic effects of metformin during nicotine withdrawal are dependent on hippocampal AMPKα. (A) Representative GFP expression in the hippocampus at 10× magnification. From left to right: GFP, DAPI, merge. (B) Western blot analysis of AMPKα and pACC in the hippocampus and cortex of AAV-Cre–treated AMPKαloxP/loxP mice indicating the specificity of gene ablation. (C) Overview of the experimental paradigm for the NIH test. Here 2-mo-old AMPKαloxP/loxP mice were injected stereotactically with AAV-Cre. Four weeks later, the mice were trained for the NIH test and treated with chronic nicotine, and NIH behavior was examined at 24 h after withdrawal from nicotine. (D) Chronic metformin treatment does not reduce anxiety in AMPKαloxP/loxP mice injected with AAV-Cre, as evidenced by an increased latency to consume a palatable food in a novel environment at 24 h after withdrawal compared with nicotine-treated AMPKαloxP/loxP mice injected with AAV-Cre. Bars represent mean latency ± SEM (n = 6–7). **P < 0.01.