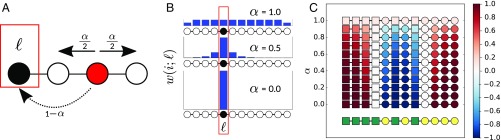
Fig. 3.
Example of the local assortativity measure for categorical attributes. (A) Assortativity is calculated (as in Eq. 1) according to the actual proportion of links in the network connecting nodes of the same type relative to the expected proportion of links between nodes of the same type. (B) The nodes in the network are weighted according to a random walk with restart probability of . (C) An example of the local assortativity applied to a simple line network with two types of nodes: yellow or green. The blue bars show the stationary distribution () of the random walk with restarts at for different values of . Underneath each distribution, the nodes in the line network are colored according to their local assortativity value.