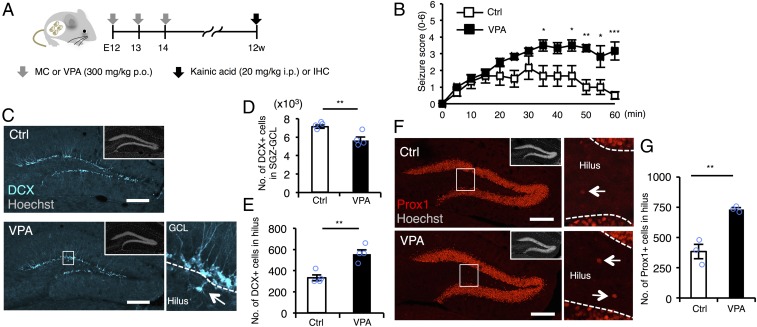
Fig. 1.
Prenatal exposure to VPA increases seizure susceptibility and ectopic hippocampal neurogenesis in the adult. (A) Experimental scheme for investigating seizure susceptibility and adult neurogenesis. Control [administered with methylcellulose (MC)] and VPA mice were randomly assigned to the groups for scoring of seizure severity and immunohistochemistry (IHC). (B) Seizure response to KA treatment over time in control and VPA mice (n = 6 animals each). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA was used for statistical analysis (treatment: F1,130 = 59.08, P < 0.0001; time: F12,130 = 7.063, P < 0.0001; treatment × time interaction: F12,130 = 2.341, P = 0.0095, post hoc Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test). (C) Representative images of DCX-positive (cyan) immature neurons in the DG. The area outlined by a white rectangle in the lower main panel is enlarged to the right. The arrow indicates a DCX-labeled cell in the hilus, and dashed white lines mark the boundaries between GCL and hilus. (Insets) H33258 nuclear staining of each field. (Scale bar, 200 µm.) (D and E) Quantification of the number of DCX-positive cells in the SGZ/GCL (D) and hilus (E) (n = 4 animals each). (F) Representative images of Prox1-positive (red) GCs in the DG. The area outlined by a white rectangle in the lower main panel is enlarged to the right. The arrow indicates a Prox1-positive cell in the hilus, and the dashed white line marks the boundary between GCL and hilus. (Insets) H33258 nuclear staining (gray) of each field. (Scale bar, 200 µm.) (G) Quantification of the number of Prox1-positive cells in the hilus (n = 3 animals each). *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001.