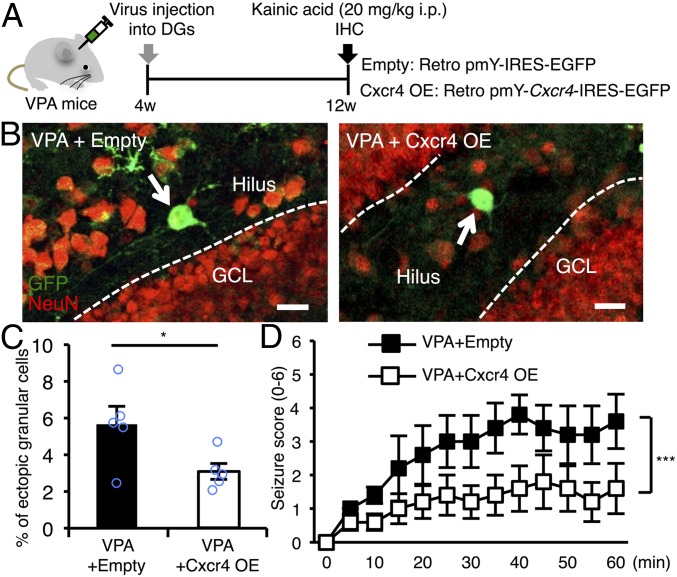
Fig. 6.
Replenishment of Cxcr4 expression in NS/PCs of the DG alleviates the increased seizure susceptibility and abnormal neuronal migration in VPA mice. (A) Experimental scheme for investigating the effect of Cxcr4 expression in NS/PCs on seizure susceptibility and neuronal migration in VPA mice. (B) Representative images of GFP (green) and NeuN (red) dual-positive (GFP+NeuN+) newborn neurons located in the hilus (arrows). Dashed white lines indicate the boundary between hilus and GCL. (Scale bar, 20 µm.) (C) Quantification of percentages of the number of ectopically located GFP+NeuN+ cells among total GFP+NeuN+ cells in the DG (n = 5 animals each). (D) Seizure response to KA treatment over time in VPA mice that received control and Cxcr4-expressing retrovirus injection (n = 5 animals each). Two-way repeated measures ANOVA was used for statistical analysis (Cxcr4: F1,104 = 33.14, P < 0.0001; time: F12,104 = 3.344, P = 0.0004; Cxcr4 × time interaction: F12,104 = 0.5549, P = 0.8731). *P ≤ 0.05, ***P ≤ 0.001.