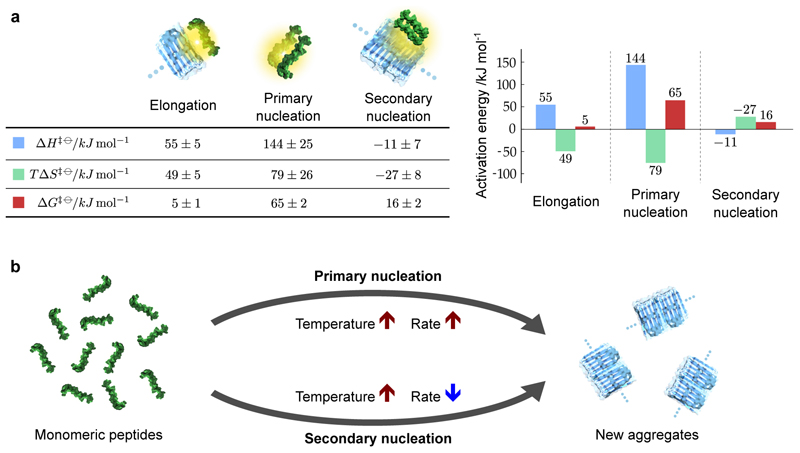
Figure 4. Activation energies of fibril elongation, primary nucleation and secondary nucleation in Aβ42 amyloid formation.
(a) The free energies of activation, and the enthalpic and entropic contributions, determined from our measurements. The activation energies for elongation and primary nucleation and primary nucleation consist of enthalpic barriers and favorable entropies of activation, whereas the enthalpic and entropic contributions to the free energy are reversed in sign for secondary nucleation. The values and standard errors shown were calculated by fitting the data shown in Fig. 3 with ΔH‡ϴ = −R ∂(log k)/∂(1/T) and ΔG‡ϴ = −RT log(k/A), which were combined to give TΔS‡ϴ = ΔH‡ϴ −ΔG‡ϴ. The entropic term is shown at T = 298K. The values are given per mole of reaction at a standard state of 1M. (b) Schematic showing the different temperature dependencies of the two nucleation processes that both generate aggregates from monomeric peptides. The structures used in the visual representations of each process are adapted from Refs. 45 and 46.