Figure 2. Lower frequency light pulses effectively drive neural activity in the motor cortex.
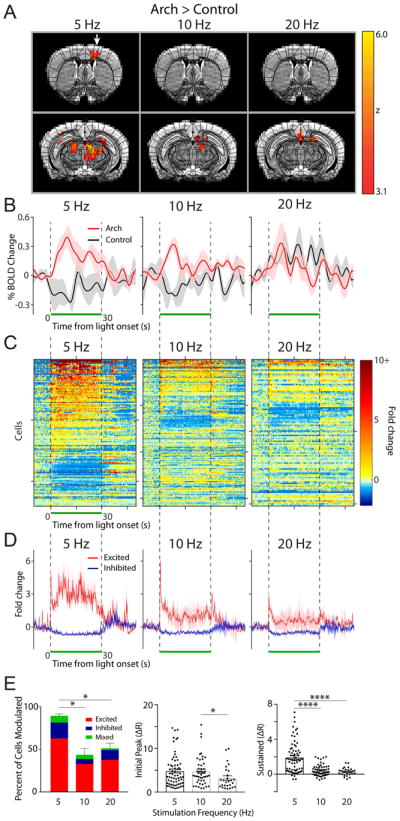
(A) OfMRI BOLD signals (Arch>control) were imaged during 10 × 30 s long epochs of 5, 10, and 20 Hz light stimulation (50% duty cycle, 143 mW/mm2 intensity) interleaved with 10 × 30 s long rest periods (no light pulse). An atlas of subdivided brain structures (black lines) is overlaid on top of the BOLD signal (yellow-red) and representative structural images (grayscale) at 2 different slice planes (Y: 0.26 and −2.7 from Bregma). White arrow points to motor cortex activation in the 5 Hz stimulation condition. (B) Time course of average percent change in BOLD activation for Arch (red, n=4–5 mice) and control (black, n=3 mice) animals stimulated at 5, 10, and 20 Hz, calculated in a subregion of the contralateral motor cortex containing significantly activated voxels in the 5 Hz Arch group (A, left). The light was pulsed during the time window indicated by the green bar. Shaded areas indicate s.e.m. (C) The fold change in baseline subtracted firing rate ((R-R0)/R0) is shown for all recorded motor cortical neurons during the 5 (n=107), 10 (n=159), and 20 (n=114) Hz stimulation period (green bar; n=3 animals). Responses are thresholded to 10× the fold rate change to improve visualization of neural activity. Starting from the top, every 50th cell is marked by a tick along the y-axis (i.e. y-axis=50 cells/tick). 200 ms/bin (D) The average neural response across cells that were significantly excited (red) and inhibited (purple) is plotted for each frequency. (E) Left, summary graph of the percent of cells modulated and the modulation type for each frequency of stimulation (one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey’s test *p<0.05). The average magnitude of the initial peak (0–4 ms, middle) and sustained increase (averaged between 10–20 ms, right) for all excited cells is plotted for each frequency (Kruskal-Wallis with post-hoc Dunn’s test *p<0.05, ****p<0.0001).
