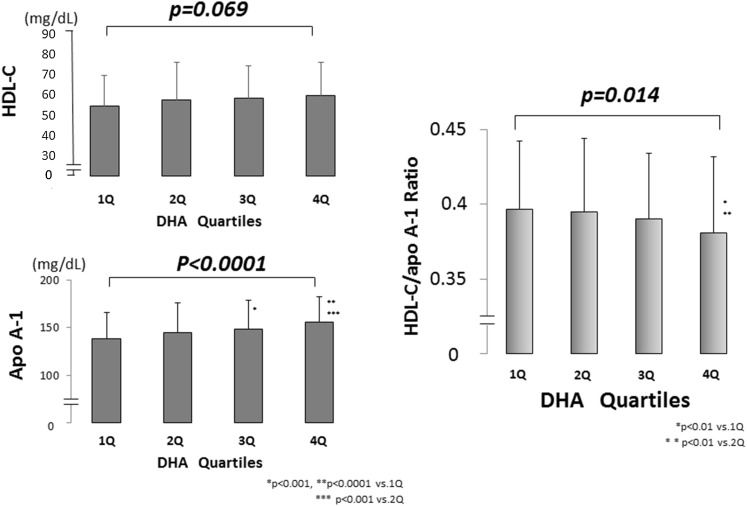
Fig. 1.
Association of the HDL-C/apoA-1 ratio with the serum DHA level. The patients were divided into quartiles of the DHA concentration. The DHA according to quartile was as follows: 35.7–100.7 μg/mL (quartile 1: n = 160), 100.8–128.7 μg/mL (quartile 2: n = 160), 128.9–160.5 μg/mL (quartile 3: n = 160), and 160.7–451.8 μg/mL (quartile 4: n = 160). The serum HDL-C level tended to increase as the serum DHA quartile increased, but it did not reach statistical significance. While the serum apoA-1 level increased significantly as the serum DHA quartile increased. The serum HDL-C/apoA-1 ratio accordingly decreased significantly as the serum DHA quartile increased. HDL-C high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, apoA-1 apolipoprotein A-1, DHA docosahexaenoic acid