Figure 3. Gene editing using site-specific endonucleases.
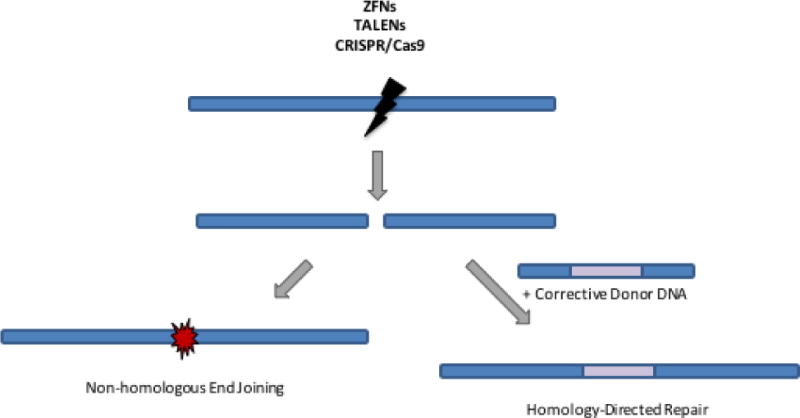
Site-specific endonucleases (ZFNs, TALENs, or CRISPR/Cas9) can be used to create targeted double stranded DNA breaks. These DNA breaks can be repaired by non-homologous end joining, which introduces small insertions and deletions and can be used for gene knockout strategies, as is employed in the CCR5 gene therapy trials for HIV. If a corrective donor DNA sequence is also provided to the cell, it can be used for homology-directed repair of the double-stranded DNA break, incorporating the therapeutic gene sequence and maintaining its expression under its endogenous regulatory elements.
