Figure 3.
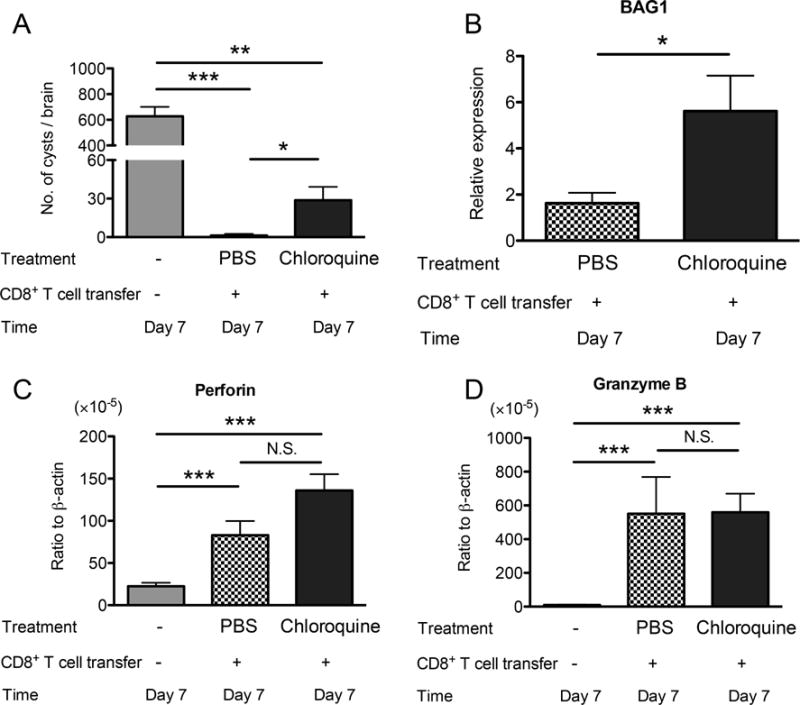
Chloroquine, the inhibitor of phagosome-lysosome system acidification, partially inhibits the immune process to remove T. gondii cysts from the brain. SCID mice were infected with 20 cysts of the ME49 perorally and treated with sulfadiazine beginning at 10 days after infection to establish a chronic infection in their brains. At 3 weeks after infection, two groups of the mice received a systemic transfer of CD8+ immune T cells (2.4 or 2.5 ×106 cells) from chronically infected BALB/c mice. One group was injected intraperitoneally with 0.6 mg of chloroquine (in 0.2 ml of PBS) daily beginning at one week before receiving CD8+ T cells for 2 weeks. Another group of infected SCID mice were injected with PBS (0.2 ml) in the same manner. Numbers of cysts (A) and amounts of BAG1 mRNA (B) were measured at 7 days after the T cell transfer (Day 7). Amounts of mRNA for perforin (C) and granzyme B (D) were also measured at Day 7. All data represent mean ± SEM. The data from two independent studies were combined. There were 6–8 mice in total in each experimental group. *Pc<0.05, **Pc<0.01, and ***Pc<0.001. N.S.: not significant.
