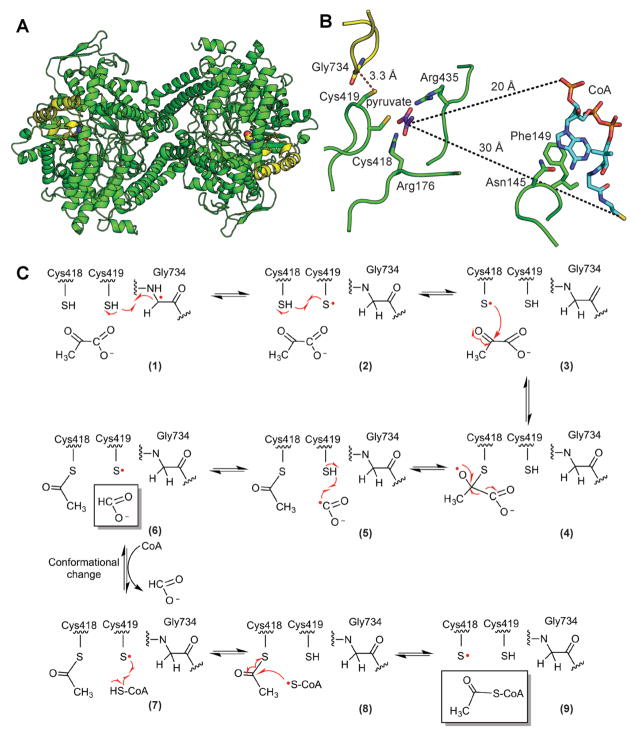
Figure 3. Structure and mechanism of PFL.
A. Ribbon drawing of the PFL homodimer with Gly radical as spheres and Gly radical domain in yellow (PDB ID: 2PFL) B. Structure of PFL with pyruvate and CoA (PDB ID: 1H16). Active site is set up for the first half reaction with Gly734 close to Cys419 and the Sγ of Cys418 close to C2 of pyruvate (2.6 Å). CoA is not in a catalytic position. It is found in the rare syn conformation, disengaged from the active site, with the CoA pyrophosphate group approximately 20 Å and the CoA thiyl group approximately 30 Å away from C2 of pyruvate. In order for the thiyl group of CoA to reach the active site to be acetylated, a dramatic conformational change must occur (Becker and Kabsch, 2002). C. Putative PFL mechanism (Becker and Kabsch, 2002). See text for discussion. A color version of this figure is available online.