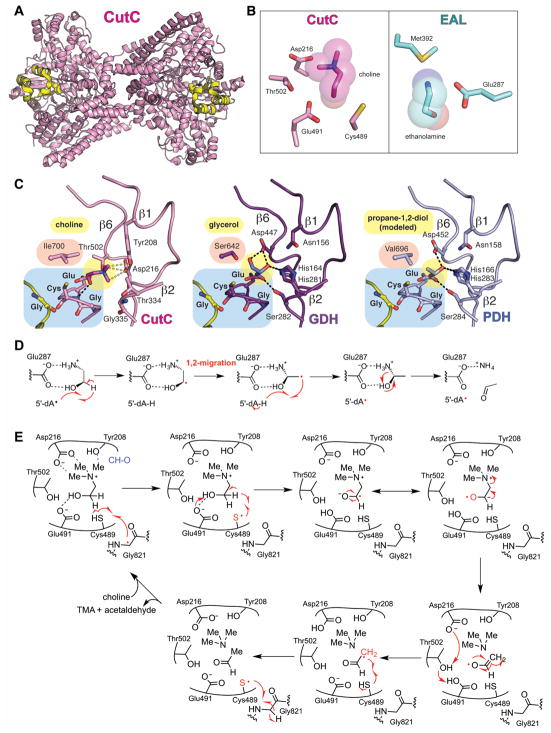
Figure 4. Structure and mechanism of GRE 1,2-eliminases.
A. Dimeric structure of CutC (pink, PDB ID: 5FAU) with Gly radical as spheres and Gly radical domain in yellow. B. Active sites of CutC with choline (pink) and AdoCbl-dependent ethanolamine ammonia-lyase with ethanolamine (EAL, teal) (PDB: 3ABO) showing that CutC has no residue that is equivalent to Glu287 or Met392 in EAL. C. Active sites of CutC, GDH, and PDH with hydrogen bonds shown as black dashed lines and CH-O interactions in CutC as gray dashed lines. Substrate positioning was determined by crystallography for CutC and GDH and is modeled for PDH. D. A proposed 1,2-migration mechanism for EAL (Wetmore et al., 2002). E. A proposed 1,2-elimination mechanism for CutC (Bodea et al., 2016). GDH and PDH are also likely to proceed through 1,2-elimination reactions. A color version of this figure is available online.