FIGURE 1.
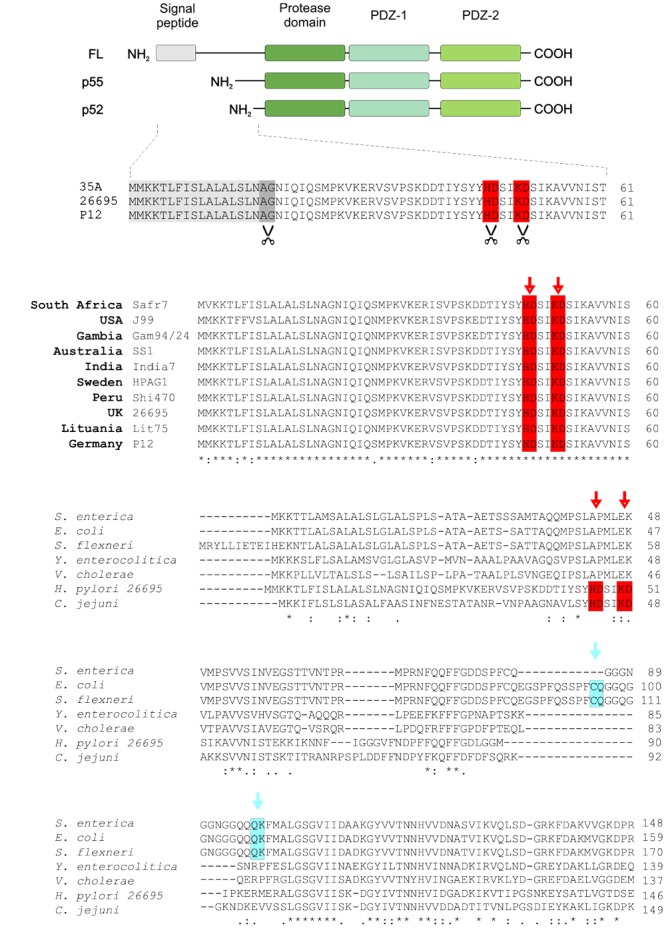
The p55 and p52 forms of HtrAHp are generated by amino-terminal cleavage and are conserved in worldwide H. pylori strains. (A) The domain structures of full-length (FL), p55 and p52 HtrAs are shown. The amino-terminal auto-processing sites, which lead to the generation of p55 and p52 forms, were identified by Edman sequencing in HtrAHp of H. pylori strains 35A, 26695, and P12. In addition to the cleaved signal peptide (gray box), cleavage sites between H46/D47 and K50/D51 (highlighted with red and scissors), respectively, were determined. (B) The amino-terminal HtrA sequences of worldwide H. pylori strains were aligned using Clustal Omega, showing that the cleavage sites H46/D47 and K50/D51 are highly conserved (red boxes). The exact cleavage positions are marked by arrows. (C) Furthermore, the amino-terminal protein sequence of HtrAHp was aligned to that of HtrAs from other Gram-negative gastrointestinal pathogens, revealing that the above cleavage sites (red boxes) are unique for H. pylori and C. jejuni. However, for the HtrA homologs from S. enterica, E. coli, and S. flexneri other amino-terminal auto-processing sites at C69/Q70 and Q82/K83 were found (marked with blue).
