FIGURE 5.
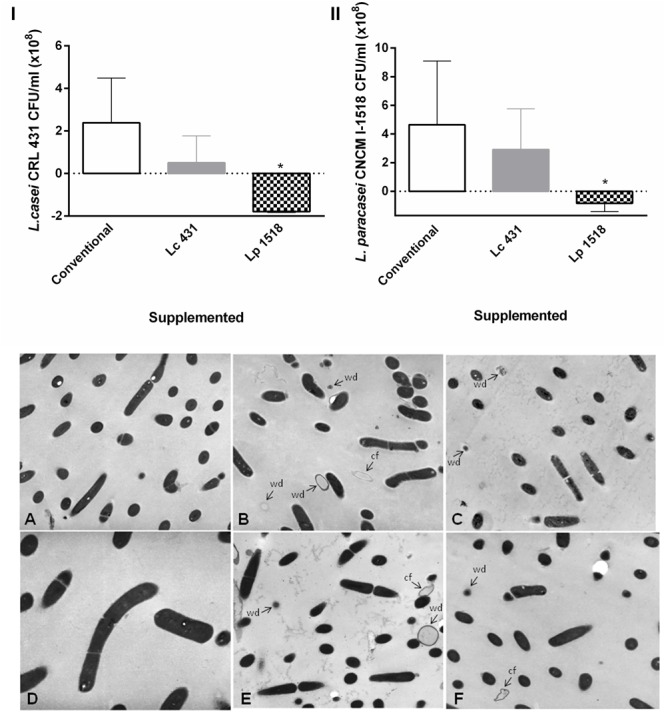
Effect of the animals’ intestinal fluids against the probiotics bacteria. In the upper panel L. casei CRL 431 (I) and L. paracasei CNCM-I 1518 (II) (108 CFU/ml) were incubated for 2 h at 37°C, in the presence of the intestinal fluids of 42 days mice fed with Conventional diet, L. casei CRL431 or L. paracasei CNCM-I 1518. After the co-incubation, viable bacteria were determined by plate count agar. Results were expressed as the differences in the CFU/ml before and after the incubation of the bacteria with the intestinal fluids. The bars represent the average of 6 determinations, and the SEM is indicated by vertical lines. ∗p < 0.05. In the panel below, transmission electron microscopy studies were performed in (A–C) L. casei CRL 431 and (D–F) L. paracasei CNCM-I 1518, incubated for 1 h at 37°C in the presence of the intestinal fluids of mice fed as indicated: Conventional diet (A,D), L. casei CRL 431 (B,E), and L. paracasei CNCM-I 1518 (C,F). Magnification (A–C,E,F: 12.800×), (D: 7.500×). cf, cell fragmentation; wd, cell walls disruption.
