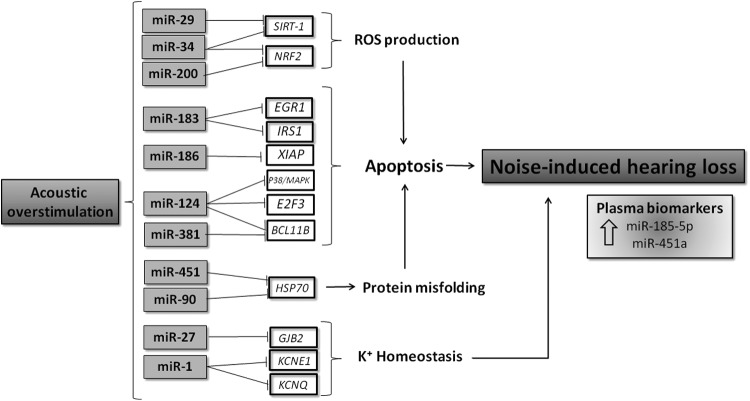
FIG. 4.
miRNAs as regulators of noise-induced hearing loss. Acoustic overstimulation mediates the expression of miRNAs that regulate genes involved in oxidative stress, potassium recycling pathways, monogenic deafness, and heat shock protein genes associated with hearing loss. Some miRNAs such as miR-124, miR-183, and miR-381 regulate apoptosis-related genes such as E2F3, EGR1, and BCL11B, respectively, whereas miR-34a and miR-29 modulate oxidative stress-related targets such as SIRT-1 and Nrf2 in the cochlea, indirectly leading to hair cell apoptosis. Other miRNAs, such as miR-27, regulate the expression of the essential protein for cochlea function, the potassium ion transporter GJB2. In addition, some miRNAs such as miR-185-5p and miR-451a have emerged as potential biomarkers in this pathology. GJB2, gap junction beta-2 protein; SIRT-1, Sirtuin-1.