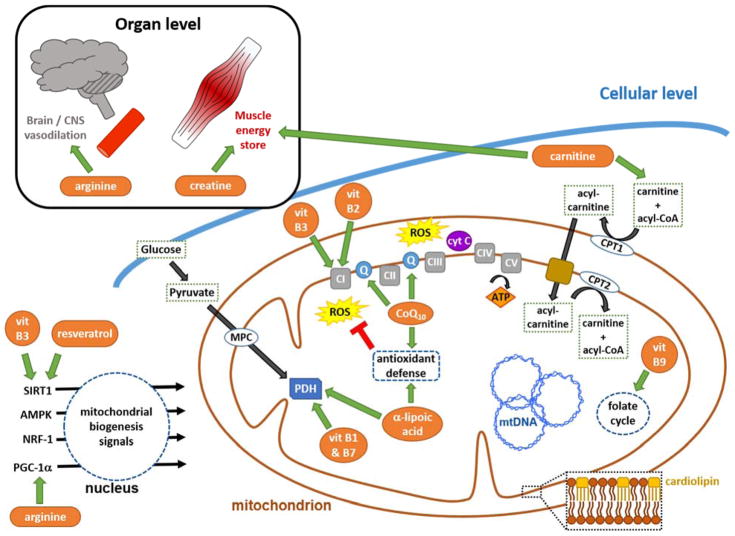
Figure 1. Mechanisms of nutritional interventions in PMDs.
At the organ level, arginine and creatine are used to improve vasodilation and energy storage. At the cellular level nutrients and metabolic modifiers and signaling activators are employed to support OXPHOS (vitamins B3 and B2, CoQ10) and metabolic pathways (vitamin B1, B7, and B9, L-carnitine, and α-lipoic acid), enhance antioxidant defenses (CoQ10 and α-lipoic acid), and promote mitochondrial biogenesis (vitamin B3, resveratrol, and arginine). Cardiolipin, dispersed throughout the mitochondrial inner membrane, is essential for optimal function of multiple metabolic enzymes. Abbreviations: CI-CV, OXPHOS complexes I-V; Q, ubiquinone; CoQ10, coenzyme Q10; CPT, carnitine palmitoyl transferase; cyt c, cytochrome c; MPC, mitochondrial pyruvate carrier; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; PDH, pyruvate dehydrogenase; ROS, reactive oxygen species, (superoxide, hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radical; vit, vitamin.