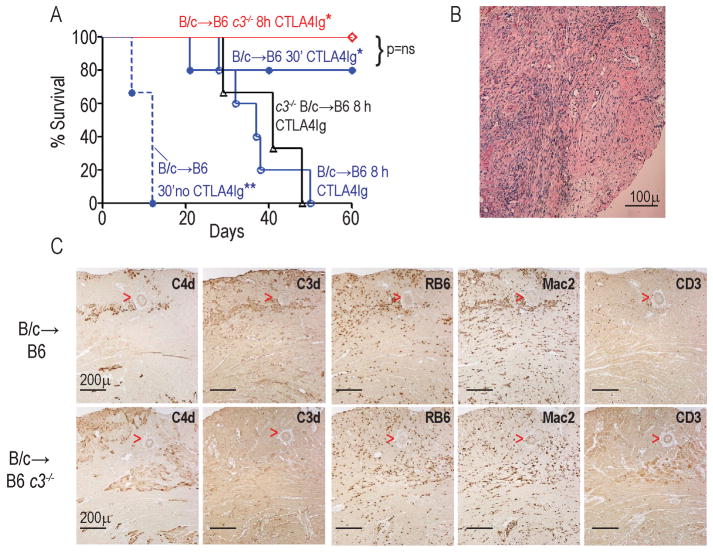
Figure 1.
Prolonged donor cold ischemia induces recipient C3-dependent, CTLA4Ig-resistant rejection A. Kaplan-Meier survival curves of WT or c3−/− BALB/c (B/c) hearts subjected to 30′ or 8h CIS and transplanted into WT or c3−/− B6 recipients (n=4–6/group). Recipients were treated with 250ug CTLA4Ig i.p. on day 0 unless indicated otherwise. *p<0.05 vs B/c→B6 8h. Graft survival in all CTLA4Ig-treated groups was longer than in untreated controls. **p<0.05 vs all conditions. B. Representative H&E stained section of B/c heart subjected to 8h CI and transplanted into a CTLA4Ig-treated B6 recipient at cessation of palpable heartbeat, demonstrating diffuse mononuclear cell infiltration consistent with cellular rejection. Scale bar=100 microns. C. Representative serial sections stained for C4d, C3d, RB6 (neutrophils), Mac2 (macrophages), and CD3 (T cells) as indicated from WT B/c hearts subjected to 8h CI 48h after transplantation into WT (upper panels) or c3−/− (lower panels) B6 recipients. Scale bar in all panels = 200 microns. Red arrowheads delineate a blood vessel. Note that the pattern of C3d and C4d staining was similar to that of RB6 and Mac2. The data are representative of allografts from at least 3 different animals per group.