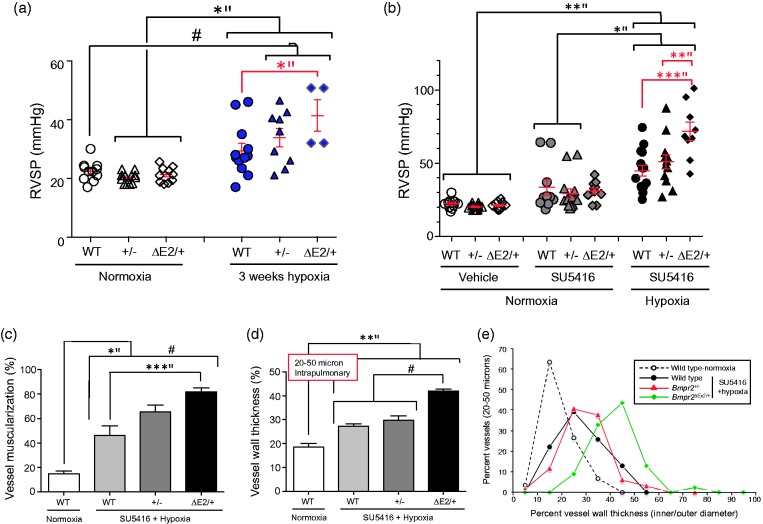
Fig. 2.
Differential susceptibility of Bmpr2+/− and Bmpr2ΔEx2/+ mutant mice to PH. (a, b) Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) measurements in male WT, Bmpr2+/−, and Bmpr2ΔEx2/+ mutant mice all maintained on a pure C57Bl/6 background ( > 10 generations) after exposure to normoxia or 10% oxygen for three weeks (a) or treatment with the VEGFR2 antagonist, SU5416 (or vehicle) subcutaneously at 20 mg/kg weekly ± 10% oxygen for three weeks, as indicated (b). RVSP measurements were obtained from pressure traces on right heart catheterization with Millar Instruments PVR-1035 pressure/volume catheters in anesthetized mice accessed via the right jugular vein. Individual data points shown, with means ± SEM indicated. (c) Peripheral muscularization. Lung sections underwent two-color immunofluorescence staining for Von Willebrand factor and α-SMA. The percent circumference of vessels covered with smooth muscle cells was determined in 20 round or oval sections of 20–50-µM diameter inter-acinar vessels per mouse. (d) Vessel wall thickness (mean of two orthogonal outer diameter–inner vessel diameters expressed as the percentage of outer diameter), measured in 10 round or oval sections of 20–50-µM diameter intrapulmonary vessels. (e) The range of vessel wall thicknesses. Individual data points represent the percentage of total vessels measured in each group with vessel wall thicknesses within the indicated ranges. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction for between-group comparisons: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; #P < 0.0001. Bars indicate statistically significant between group differences. Figure modified from Figs. 2 and 3 in Frump et al. with permission from the publishers.27