Figure 2.
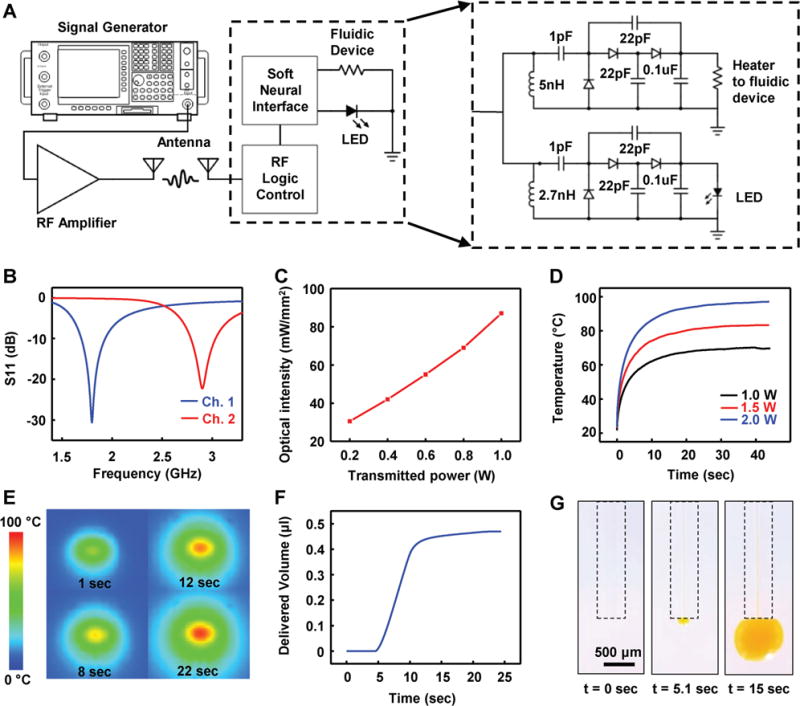
Electrical, optical, and thermal characteristics of battery-free, wireless optofluidic systems with two-channel stretchable antennas. A) Schematic diagram showing the overall setup for operation of a two-channel wireless optofluidic system (left) and its detailed circuit diagram (right). B) Scattering parameter S11 of the two-channel antenna (channel 1, blue; channel 2, red). C) Optical intensity of μ-ILEDs as a function of RF power transmitted from 10 cm away. D) Heater temperature variation with different RF power transmissions. E) Time sequence of IR images of the heater showing the temperature increase. F) Delivered fluid volume as a function of time when 2 W of the RF power is transmitted. G) Sequential images of fluid delivery through a microfluidic probe.
