Figure 2. High-throughput TCR sequencing.
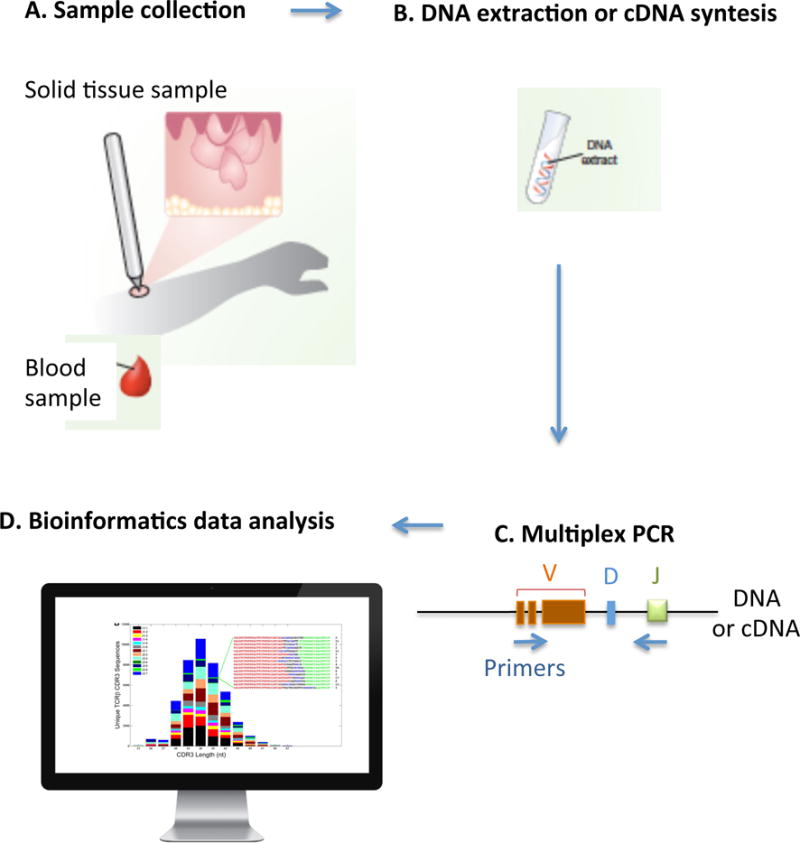
A) The biologic sample of interest is collected. B) DNA is extracted or complementary DNA (cDNA) is synthetized. C) Bias-controlled multiplexed PCR amplifies and sequences the CDR3 from the DNA or cDNA. Then, bias-controlled V and J gene primers are used to amplify the rearranged V(D)J segments. D) Bioinformatics can then be used to identify, quantify and track each individual lymphocyte as well as the entire repertoire within any sample of interest. It is possible to identify and quantify the unique CD3 segments and the V, D, and J genes within each rearrangement, based on previously described sequences incorporated in data banks.
