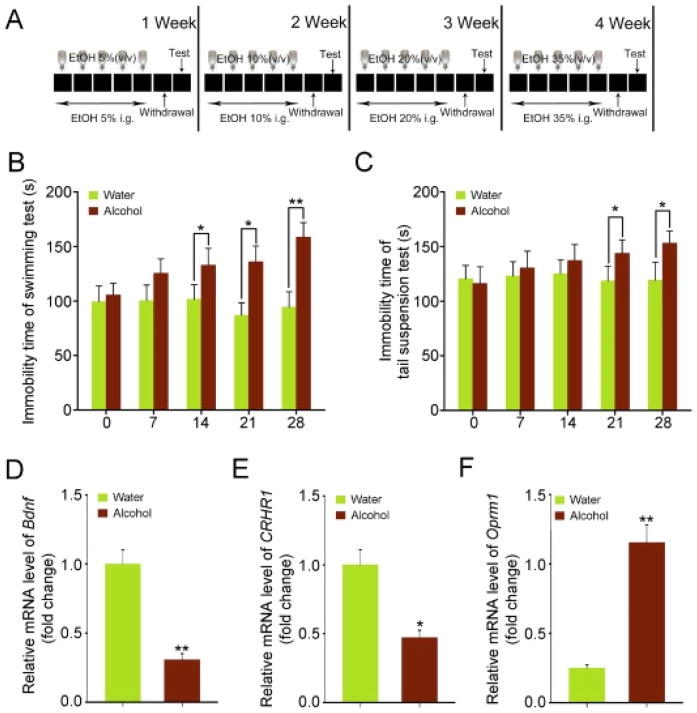
Fig. 1. The successful establishment of murine model of chronic alcoholism.
(A) Scheme for experimental protocol. (B, C) The effects of chronic alcohol consumption on cognitive functions. The forced swimming test (B) and tail suspension test (C) were performed at day 7, 14, 21 and 28. (D– F) The expression levels of Bdnf (D), CRHR1 (E) and Oprm1 (F) in the hippocampus were assessed at day 28 by qRT-PCR, n = 6 per group. Statistically significant differences are indicated: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; Student’s t-test.