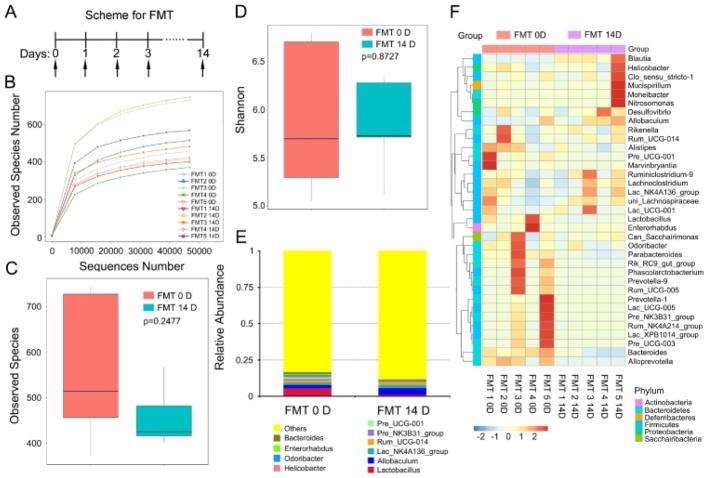
Fig. 4. Faecal microbiota transplantation from the alcohol-fed mice did not affect the abundance of gut bacterial in the recipients.
(A) Scheme for faecal microbiota transplantation. (B–D) The observed species number (B, C) and Shannon diversity index (D) of intestinal bacteria in mice before (FMT 0D) and after (FMT 14D) alcohol-fed mice’s stool supernatant treatment was assessed by 16S RNA sequencing, n = 5 per group. The top and bottom boundaries of each box indicate the 75th and 25th quartile values, respectively, and lines within each box represent the 50th quartile (median) values. Ends of whiskers mark the lowest and highest diversity values in each instance. (E, F) The alteration of intestinal bacterial patterns at the genus level in mice before (FMT 0D) and after (FMT 14D) alcohol-addicted mice’s stool supernatant treatment was assessed by 16S RNA sequencing, n = 5 per group. Statistically significant differences are indicated: Student’s t-test. The heatmap is colour-based on row Z-scores.