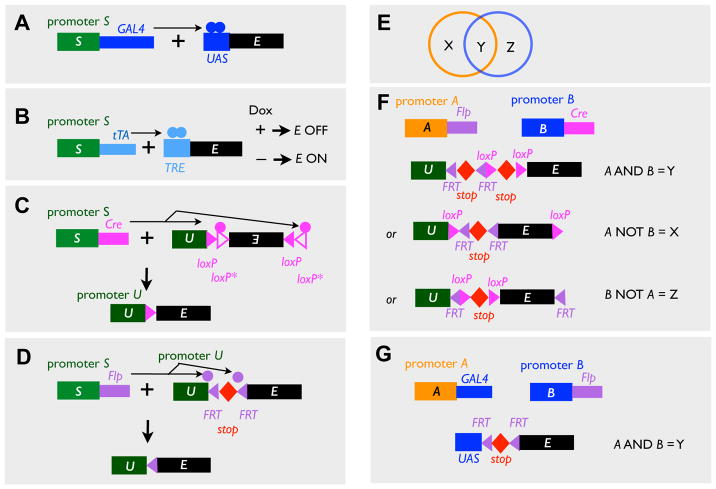
Figure 1. Binary Expression and Intersectional Strategies.
(A–B) Transcription-based binary expression systems. In the driver transgenes, coding sequences for the transcription factor GAL4 (A) and tTA (B) are driven from a cell type-specific promoter (S). In the responder transgenes, the coding sequence of the effector (E) is driven by promoters that contain binding sites of the transcription factors in the driver transgenes, UAS (A) and TRE (B). Note that tTA/TRE system can be further regulated by the drug Dox.
(C–D) Recombinase-based binary expression systems. In the driver transgenes, coding sequences for the recombinase Cre (C) and Flp (D) are driven from a cell type-specific promoter (S). In the responder transgenes, the effector is only expressed after Cre or Flp acts on the loxP or FRT sites to invert the intervening sequence (C), or to remove the transcription stop between the ubiquitous promoter (U) and the coding sequence of the effector (D). Note that both strategies can be applied to Flp/FRT- and Cre/loxP- mediated activation. The inversion strategy (C, where the recombinase recognition sites are in opposite direction as indicated by the triangles) utilizes two variants of recombinase recognition sites (here loxP and loxP*) that can only support recombination between the same variant. This strategy is termed FLEx (Schnutgen et al., 2003).
(E) Overlapping expression driven from promoter A (orange) and B (blue) creates three patterns, X, Y, and Z, which can be accessed by intersectional strategies in F and G.
(F) Intersectional strategies based on two recombinases driven from promoters A and B.
In the “A AND B” strategy, the effector is only expressed after Flp- and Cre-mediated recombination both occur, removing the two intervening transcriptional stops.
In the “A NOT B” strategy, the action of Flp removes the stop and thus activates the effector, whereas the action of Cre deletes the coding sequence of the effector, thus inactivates it.
The “B NOT A” strategy is similar to the “A NOT B” strategy except that the FRT and loxP sites are switched.
(G) AND gate can also be achieved by combining a recombinase and a transcription system.