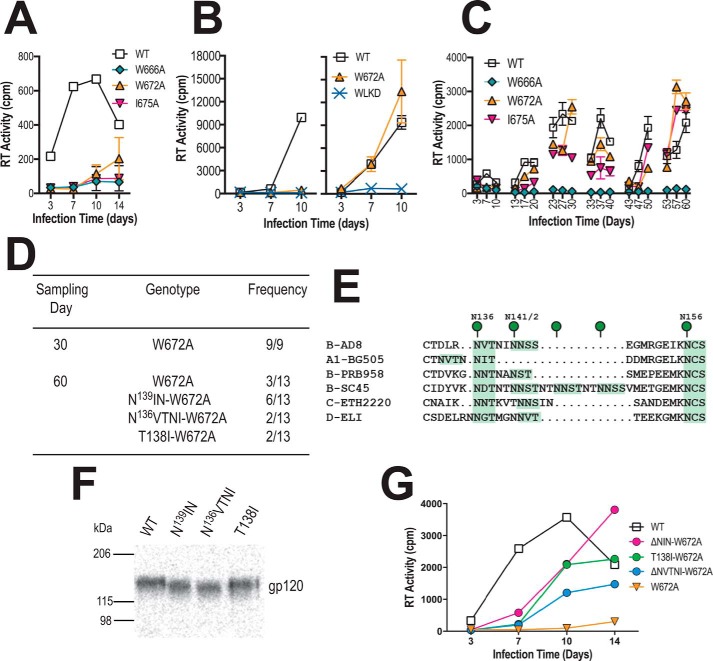
Figure 8.
In vitro evolution of pAD8-W672A. A, 14-day replication kinetics of WT and mutated AD8 viruses. Virus stocks produced in 293T cells were normalized according to RT activity and used to infect PHA-stimulated PBMCs. RT activity was measured in culture supernatants obtained at days 3, 7, 10, and 14 postinfection. The mean RT activity ± S.D. of duplicate samples is shown. B, U87.CD4.CCR5 cells were inoculated with unpseudotyped (left panel) or VSV G-pseudotyped (right panel) HIV-1AD8 particles (50,000 cpm of RT activity per inoculum) and then trypsinized 24 h later to remove residual adsorbed virus. The cells were then replated and cultured for a further 10 days. Mean RT activity ± S.D. of triplicate samples is shown. Data are representative of two independent experiments. C, long-term PBMC culture of WT and mutated AD8 viruses. Viruses produced by transfected 293T cells were normalized according to RT activity prior to infection of PHA-stimulated PBMCs. The PBMCs used in each passage were obtained from different donors. Cell-free virus collected at day 10 of each passage was normalized for RT activity and used to infect fresh PHA-stimulated PBMCs. The mean RT activity of duplicate samples is shown. D, frequency of genotypes observed in env clones obtained at days 30 and 60 from the W672A culture. E, alignment of V1 sequences, with potential N-linked glycosylation sites highlighted in green. F, migration of immunoprecipitated 35S-labeled gp120 molecules containing second site mutations in SDS-PAGE. G, 14-day replication kinetics of HIV-1AD8-W672A viruses ± 2nd site mutations in V1. Virus stocks produced in 293T cells were normalized according to RT activity and used to infect PHA-stimulated PBMCs. RT activity was measured in culture supernatants obtained at days 3, 7, 10, and 14 postinfection. The mean RT activity of duplicate samples is shown.