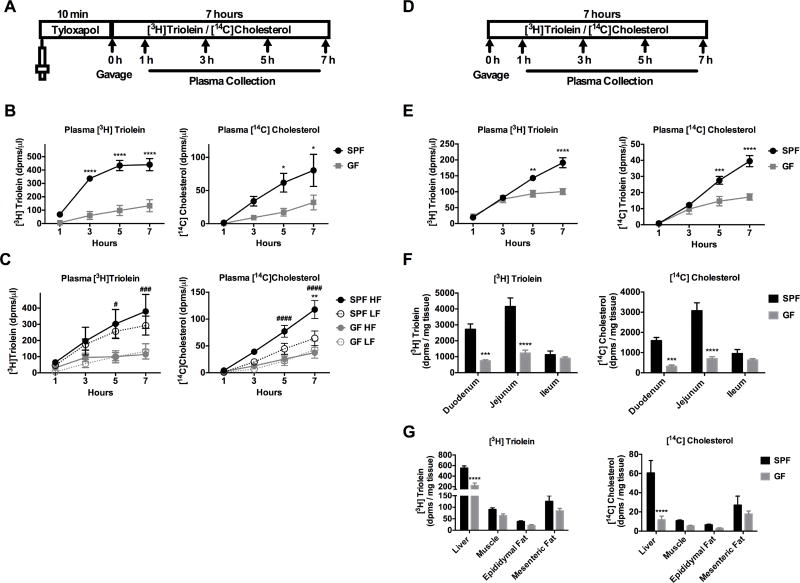
Figure 2. GF mice have impaired lipid absorption and transport compared to SPF mice.
A) Schematic of experimental procedure is shown. Mice were treated for 10 minutes with (A–C) or without (E–G) tyloxapol followed by gavage with [3H]triolein and [14C]cholesterol. B) Radiolabeled lipid absorption was measured in SPF and GF mice that were fed a standard chow diet. C) Radiolabeled lipid absorption was measured in mice that were fed a low fat (LF) or high fat (HF) diet for 4 weeks. D) Schematic of experimental procedure without tyloxapol is shown. E) Radiolabeled lipid absorption was measured in SPF and GF mice fed a standard chow diet. F–G) Radiolabeled lipid was measured in intestinal epithelium or metabolic tissues. See also Figure S2. Data were pooled across 1–3 independent experiments and are shown as means +/− SEM (n= 7–9 B; n=5–11 C; n=5–6 E–G). B, E–G) * p ≤ 0.05 (SPF vs GF). C) * p ≤ 0.05 (LF vs HF), # p ≤ 0.05 (SPF vs GF).