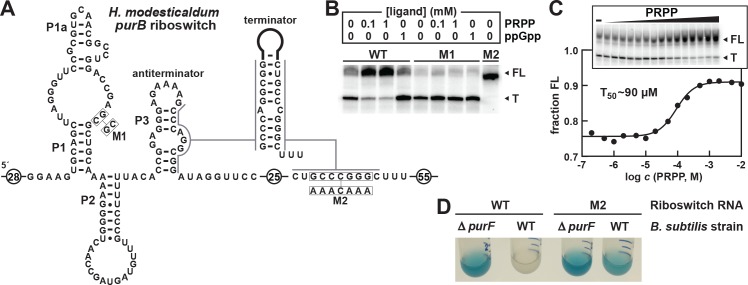
Figure 3. Transcription regulation and reporter gene expression by a natural singlet PRPP riboswitch.
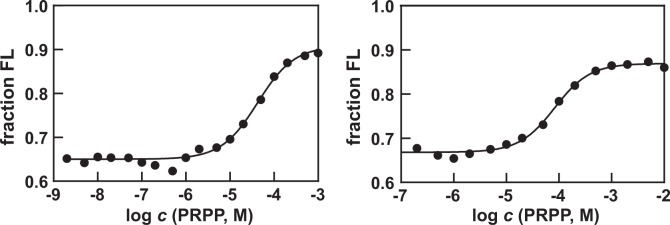
(A) Sequence and secondary structure of the natural PRPP singlet riboswitch derived from the purB gene from H. modesticaldum. An alternative RNA structure is depicted in which the terminator stem forms followed by a U-rich tract, which only forms in the absence of PRPP. (B) PAGE analysis of a single-round transcription termination assay of WT and mutant H. modesticaldum purB riboswitches at the indicated ligand concentration. FL and T denote full length and terminated transcripts, respectively. Values for the fraction of full-length transcripts relative to the total transcription yield is listed for each reaction. (C) Plot of the fraction of full length WT H. modesticaldum purB RNA riboswitch transcripts contributing to the total number of transcripts (FL plus T) as a function of the logarithm (base 10) of the molar PRPP concentration. The concentration of PRPP required to cause half-maximal termination efficiency (T50) was determined by a sigmoidal curve fit (see METHODS). Inset: PAGE analysis of single round transcription termination assays of the WT H. modesticaldum purB RNA with either no ligand (–) or PRPP ranging from 200 nM to 10 mM. Data for replicates of this transcription termination assay are presented in Figure 3—figure supplement 1. (D) Reporter gene expression of WT and ΔpurF [BKE06490 (depicted) and BKK06490 (not shown)] B. subtilis cells containing wild-type (WT) or mutant (M2) H. modesticaldum purB riboswitch-lacZ reporter fusion constructs as described in A. Cells were grown in glucose minimal medium (GMM) containing 50 µg mL-1 X-gal.