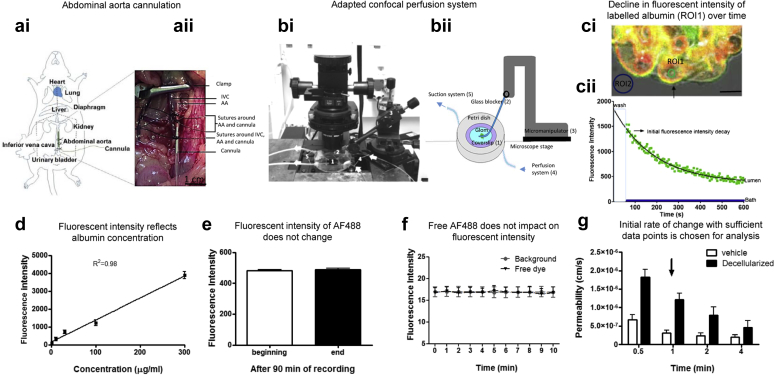
Figure 1.
Glomerular albumin permeability assay setup and characterization. (a) A midline laparotomy was used to expose the abdominal aorta, which was cannulated with a blunted needle, as detailed in (i) and (ii). AA, abdominal aorta; IVC, inferior vena cava. (bi) The photograph shows an inverted confocal microscope equipped with a modified Petri dish consisting of a central hole with a glass coverslip (0.085-mm thickness) attached on the top and connected to a perfusion and a suction system. Glomeruli were trapped on the (1) glass coverslip by a (2) glass restrainer positioned using a (3) micromanipulator. Ringer bovine serum albumin (BSA) was pumped into the Petri dish though a (4) perfusion system and simultaneously removed though a (5) suction system to wash the glomeruli of surrounding Alexa Fluor 488 (AF488) BSA (20–60 seconds). Arrows indicate the direction of flow. A schematic is shown to reflect the setup showing a glomerulus trapped by a micromanipulator connected to a restraining glass pipette. (bii) Numbers relate to those shown in (bi). (ci) An image of peripheral capillary loops of a trapped glomerulus is shown. The capillary wall is labeled red with R18, and AF488-BSA fills the lumen (labeled yellow where there is colocalization). The arrow indicates a spherical capillary, chosen for analysis. Region of interest (ROI) 1 and ROI2 are shown in the capillary lumen and bath, respectively (bar = 5 μM). (cii) The decline in fluorescence intensity of labeled albumin over time is plotted. The green boxes represent the flux of movement of fluorescently labeled albumin molecules from the lumen to the bath (ROI1), and the blue line represents the fluorescence intensity of the bath after the wash (ROI2). The decline in fluorescence intensity follows a single exponential decay (green boxes, r2 = 0.97). (d) Mean fluorescence intensity was plotted against AF488-BSA concentrations. (e) The initial fluorescence intensity values were compared with the FI values at the end of the experiment (after 90 minutes of laser exposure; paired t test, P = 0.20). Free dye fluorescence intensity is plotted against time and is not different than background. (f) Permeability between decellularized and normal (vehicle-treated) glomeruli were analyzed for different periods of time following the washout period. (g) The period chosen for analysis after the washout period was 1 minute (arrow) because this had a significant number of frames to analyze (30 seconds was too few) and differentiated well between treatment groups. To optimize viewing of this image, please see the online version of this article at www.kidney-international.org.