Figure 2.
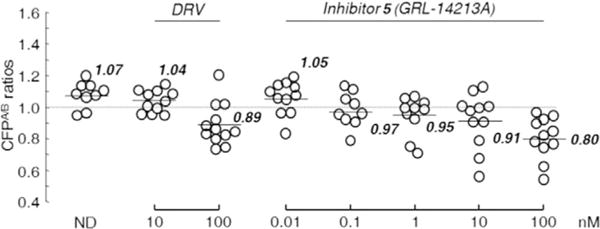
Inhibition of HIV-1 protease dimerization activity by GRL-14213A. COS-7 cells were exposed to various concentrations (0.01–100 nm) of GRL-142 or DRV and were subsequently co-transfected with two plasmids, pHIV-PRWT-CFP and pHIV-PRWT-YFP, respectively. After 72 h, cultured cells were examined in the FRET-based HIV-1 expression assay, and the CFPA/B ratios (y axis) were determined. The arithmetic mean values of the ratios obtained are shown as horizontal bars. A CFPA/B ratio >1 signifies protease dimerization, whereas a ratio <1 signifies disruption of protease dimerization. All experiments were conducted in a blind fashion. P values were determined using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (JMP software, SAS, Cary, NC, USA) and were 0.3816 for the CFPA/B ratio in the absence of drug (CFPA/BNo-Drug) versus the CFPA/B ratio in the presence of 10 nm DRV (CFPA/B10-DRV), 0.004 for CFPA/BNo-Drug versus CFPA/B100-DRV, 0.8192 for CFPA/BNo-Drug versus CFPA/B0.01-GRL-142, 0.0459 for CFPA/BNo-Drug versus CFPA/B0.1-GRL-142, 0.0197 for CFPA/BNo-Drug versus CFPA/B1-GRL-142, 0.0248 for CFPA/BNo-Drug versus CFPA/B10-GRL-142, and 0.0003 for CFPA/BNo-Drug versus CFPA/B100-GRL-142.
