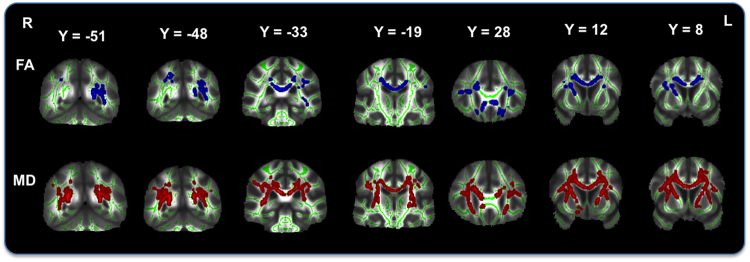
Figure 5.
Post-hoc t-tests of Framingham stroke risk and lower white matter integrity. Post-hoc t-tests show an associations of higher Framingham stroke risk with lower fractional anisotropy (FA; top) and higher mean diffusivity (MD; bottom) after removing the effects of metabolic syndrome, allostatic load index and socio-demographic variables. Significant fractional anisotropy voxels extend bilaterally in the corona radiata, corpus callosum, forceps major, superior longitudinal fasciculus, in the right hemisphere along the anterior thalamic radiation, corticospinal tract and internal capsule, as well as in the left inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus and posterior thalamic radiation. Significant mean diffusivity voxels are present in similar regions but more widespread and less lateralised than with fractional anisotropy. Results represent voxels significant at p < 0.05, threshold-free cluster enhancement, multiple comparisons corrected. Significant regions are dilated for illustrative purposes, overlaid on a green skeleton. R, right; L, left. Coordinates are in MNI space.