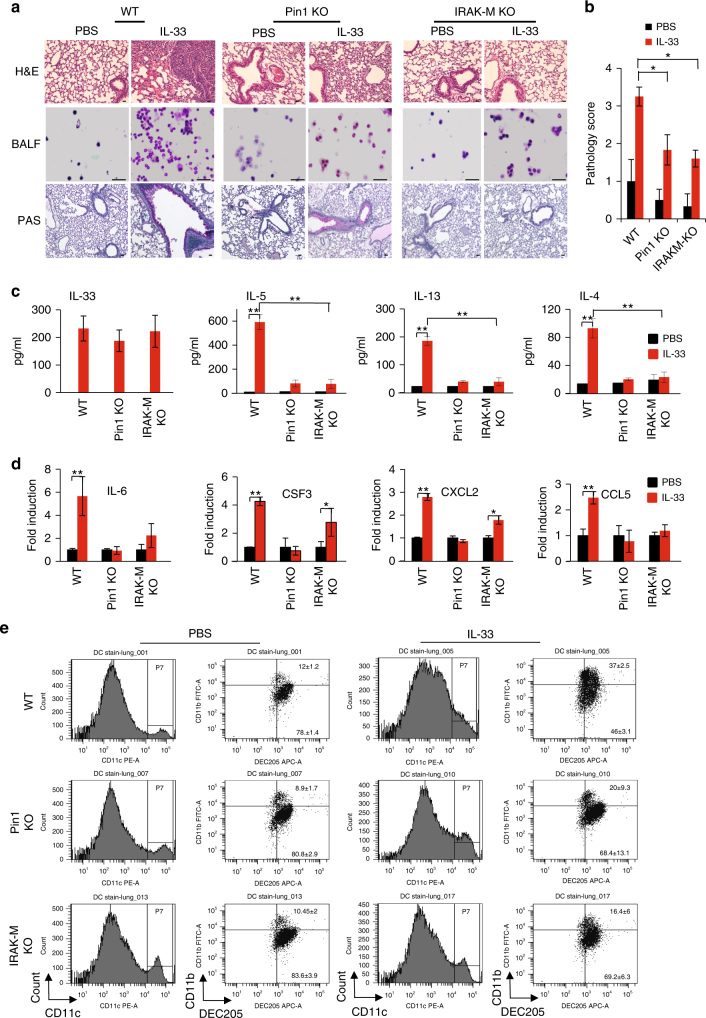
Fig. 6.
IRAK-M KO and PIN1 KO dramatically reduce lung inflammation upon IL-33 treatment in vivo. a Representative H&E, PAS staining of lung sections from various treated mice, as well as BALF cytospin from the treated mice stained with Giemsa stain (n = 5). Scale bar = 50 µm. b Histopathology score- All H&E and PAS histological samples were examined and scored in a blind manner by the core facility pathologist (n = 5). c ELISA measurements of IL-33, -5, -13 and IL-4 in the BALF of the mice treated with PBS or IL-33. d RNA was obtained from the whole lung tissue and analyzed for the relative expression of Il6, Csf3, Cxcl2 and Ccl5 by qRT-PCR. e CD11c+ CD11b+ CD205+ cells were monitored after PBS or IL-33 challenge in the indicated mice (n = 3). In WT mice there was a 3-fold induction (P < 0.05) in CD11c+ CD11b+ CD205+ cells upon IL-33 treatment. PIN1 KO mice showed a more moderate increase and IRAK-M KO mice showed non significant (NS) increase in the CD11c+ CD11b+ CD205+ cells upon IL-33 treatment. The data were analyzed by a Student’s two-tailed t test and the values are reported as mean ± standard errors of the means (SEM). *- statistical significance (P < 0.05), **- significance (P < 0.01)