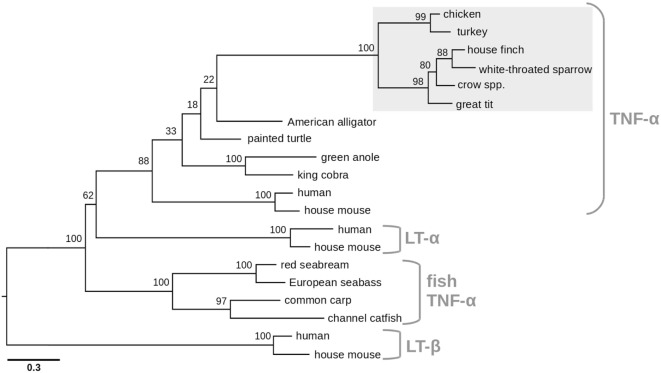
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic relationship of avian tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α proteins with other members of the TNF superfamily. The maximum likelihood tree was generated from avian TNF-α proteins for which full-length sequences were obtained in this study, together with selected vertebrate TNF-α proteins and representatives of lymphotoxin-α (LT-α) and lymphotoxin-β (LT-β) families. TNF-α proteins include the representatives presented in Figure 1, along with avian sequences from this study (turkey, Meleagris gallopavo; house finch, Haemorhous mexicanus; white-throated sparrow, Zonotrichia albicollis; crow spp., Corvus spp.; great tit, Parus major) and fish sequences: red seabream (Pagrus major; AAP76392), European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax; AAZ20770), common carp (Cyprinus carpio; CAC84641), and channel catfish (Ictalurus punctatus; NP_001187101). LT-α sequences include human (NP_000586) and house mouse (NP_034865), LT-β include human (NP_002332) and house mouse (NP_032544). Bootstrap support values are shown for each node. The scale bar indicates the number of amino acid substitutions per site.