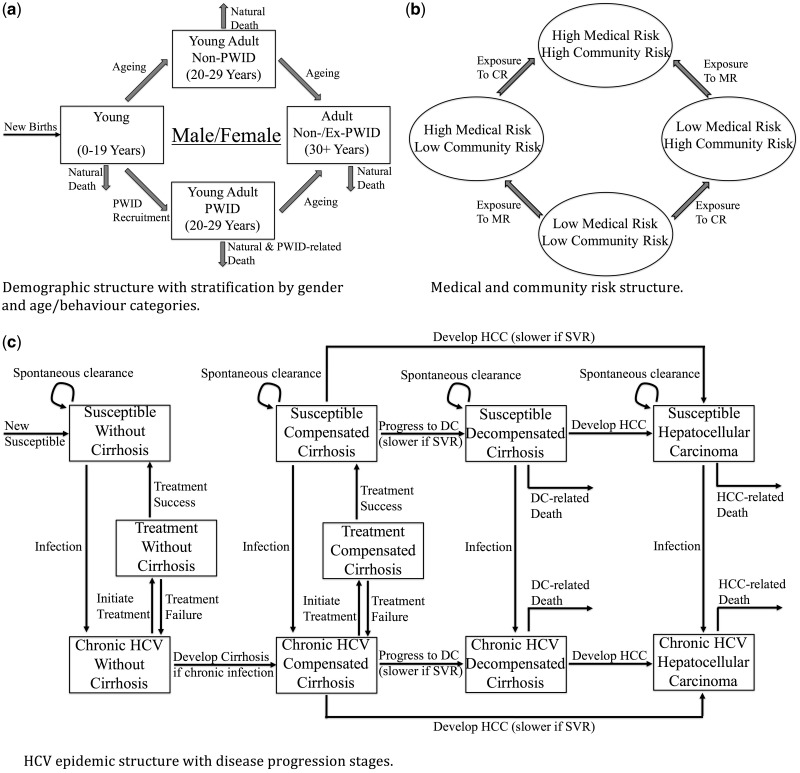
Figure 1.
A schematic illustration showing the structure of the full mathematical model, which incorporates (a) demographic characteristics of the population, including stratification by gender and age, (b) medical and community risk factors that contribute to HCV transmission, and (c) the infection dynamics of the HCV epidemic with disease progression stages. High medical risk is defined as having either over 5 therapeutic injections in the last year, history of blood transfusions, surgery, or haemodialysis, whereas high community risk is defined as ever barbering (males), ear/nose piercings (females), tattoo/acupuncture, or sharing smoking equipment. HCV: hepatitis C virus; PWID: people who inject drugs; DC: decompensated cirrhosis; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; CR: community risks; MR: medical risks; SVR: sustained virologic response.