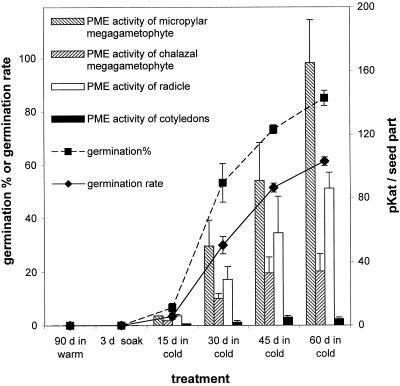
Figure 5.
A comparison of PME activities and germination capacity of yellow cedar seeds. Mature seeds were subjected to a 3-d soak (only) or to a 3-d soak and 30 d of warm, moist conditions followed by different periods of moist chilling (15, 30, 45, or 60 d, the latter representing the full dormancy-breaking treatment). As a control, seeds were subjected to a 3-d soak followed by 90 d of warm, moist conditions. At the times indicated, one set of seeds was assayed for PME activity, and the remainder of the seeds were placed in germination conditions for 30 d to monitor the germination capacity (rate and percentage of germination). Data are based on three replicates of 10 seed parts for PME activities or on three replicates of 20 seeds each for germination measures (±se). Germination rate indicates the speed of germination and was calculated according to the formula noted in “Materials and Methods.”