FIGURE 1.
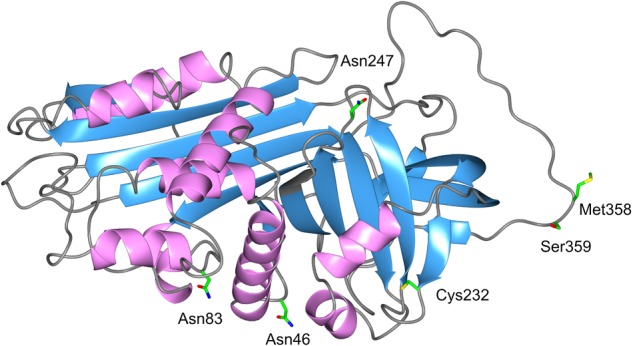
3D structure of AAT. The AAT protein is a 394-amino acid peptide with one free cysteine residue (marked in the structure) and three asparagine-linked carbohydrate side-chains at positions 46, 83, and 247. The AAT polypeptide chain is arranged into structural elements consisting of three beta-sheets (blue color) and nine alpha-helices (purple color), each formed by the first 150 residues. A reactive center loop presents the key Met358–Ser359 (P1-P1′) residues for the cleavage by the target proteases. This active site designated “P1 residue” is responsible for the anti-protease activity and specificity of the inhibitor. Side chains of amino acids of interest are colored as carbon (green), oxygen (red), nitrogen (blue), and sulfur (yellow).
