Figure 1.
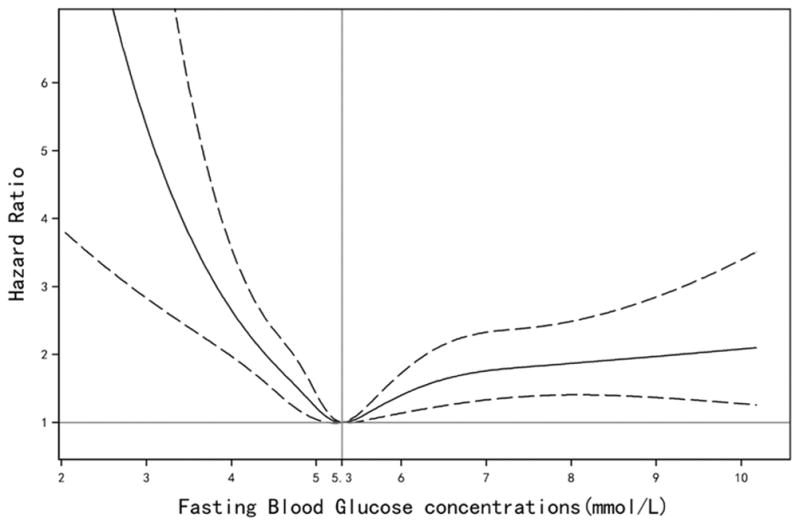
Adjusted hazard ratios of intracerebral hemorrhage according to updated cumulative average fasting blood glucose concentration. Model adjusted for age, sex, smoking, alcohol intake, education, physical activity, average monthly income of each family member, sodium intake, updated use of antihypertensive, aspirin, hypoglycemic, and lipid-lowering medications, and updated cumulative average body mass index, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, high sensitive C-reactive protein, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, and estimated glomerular filtration rate. Data were fitted by a restricted cubic spline Cox proportional hazards model. The 95% confidence intervals are indicated by the dashed lines.
